Unconscious goal pursuit strengthens voluntary force during sustained maximal effort via enhanced motor system state
- PMID: 39553609
- PMCID: PMC11566863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39762
Unconscious goal pursuit strengthens voluntary force during sustained maximal effort via enhanced motor system state
Abstract
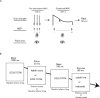
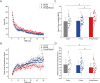
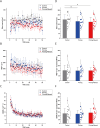
Maximal voluntary force is known to be enhanced by shouting during sustained maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) via the enhancement of motor cortical excitability. However, whether excitatory input to the primary motor cortex from areas other than the motor-related cortical area induces muscular force-enhancing effects on the exertion of sustained maximal force remains unclear. Therefore, by examining motor evoked potentials to transcranial magnetic stimulation during sustained MVC and assessing handgrip force, the present study aimed to investigate the effects of subliminal goal-priming with motivational rewards on the state of the motor system. The findings revealed that when combined with rewards in the form of a consciously visible positive stimulus, barely visible priming of an action concept increased the maximal voluntary force and reduced the silent period (i.e., reduced motor cortical inhibition). To our knowledge, this is the first study to report a link between the muscular force of subliminal reward-goal priming during MVC and the enhancement of motor system activity through subliminal reward-goal priming operating on the motor system, possibly through the potentiation of activity of the reward-linked dopaminergic system.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

