Biosynthesis of nanoparticles using microorganisms: A focus on endophytic fungi
- PMID: 39553612
- PMCID: PMC11564013
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39636
Biosynthesis of nanoparticles using microorganisms: A focus on endophytic fungi
Abstract
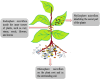
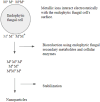
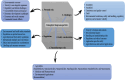
The concept of this review underscores a significant shift towards sustainable agricultural practices, particularly from the view point of microbial biotechnology and nanotechnology. The global food insecurity that causes increasing ecological imbalances is exacerbating food insecurity, and this has necessitated eco-friendly agricultural innovations. The chemical fertilizers usage aims at boosting crop yields, but with negative environmental impact, thus pushing for alternatives. Microbial biotechnology and nanotechnology fields are gaining traction for their potential in sustainable agriculture. Endophytic fungi promise to synthesize nanoparticles (NPs) that can enhance crop productivity and contribute to ecosystem stability. Leveraging on endophytic fungi could be key to achieving food security goals. Endophytic fungi explore diverse mechanisms in enhancing plant growth and resilience to environmental stresses. The application of endophytic fungi in agricultural settings is profound with notable successes. Hence, adopting interdisciplinary research approaches by combining mycology, nanotechnology, agronomy, and environmental science can meaningfully serve as potential pathways and hurdles for the commercialization of these biotechnologies. Therefore, setting regulatory frameworks for endophytic nanomaterials use in agriculture, by considering their safety and environmental impact assessments will potentially provide future research directions in addressing the current constraints and unlock the potential of endophytic fungi in agriculture.
Keywords: Antifungal; Biogenesis; Nano-biotechnology; Nano-enabled agriculture; Nano-structure; Plant yield component.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Co-author, Prof. Damian C. Onwudiwe is serving in an editorial capacity (Associate Editor) for the Heliyon and was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article. Therefore, the authors declare that they have no competing interests. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Singh A.V., Shelar A., Rai M., Laux P., Thakur M., Dosnkyi I., Santomauro G., Singh A.K., Luch A., Patil R., Bill J. Harmonization risks and rewards: nano-QSAR for agricultural nanomaterials. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024;72:835–2852. - PubMed
-
- Adeleke B.S., Akinola S.A., Adedayo A.A., Glick B.R., Babalola O.O. Synergistic relationship of endophyte-nanomaterials to alleviate abiotic stress in plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022;10
-
- Sah M.K., Thakuri B.S., Pant J., Gardas R.L., Bhattarai A. The multifaceted perspective on the role of green synthesis of nanoparticles in promoting a sustainable green economy, Sustainable. Chem. 2024;5:40–59.
-
- Saratale R.G., Saratale G.D., Shin H.S., Jacob J.M., Pugazhendhi A., Bhaisare M., Kumar G. New insights on the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant and waste biomaterials: current knowledge, their agricultural and environmental applications. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2018;25:10164–10183. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

