Advancements and challenges in Arabic sentiment analysis: A decade of methodologies, applications, and resource development
- PMID: 39553679
- PMCID: PMC11564071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39786
Advancements and challenges in Arabic sentiment analysis: A decade of methodologies, applications, and resource development
Abstract
The exponential growth of digital information, particularly user-generated content on social media and blogging platforms, has underscored the importance of sentiment analysis (SA). Arabic language sentiment analysis (ASA) involves identifying the orientation of ideas, feelings, emotions, and attitudes within Arabic text to determine whether they convey a positive, negative, or neutral sentiment. This paper presents a comprehensive review of the past decade, focusing on the utilization of SA in the Arabic language. It examines various applications, methodologies, and challenges associated with ASA, highlighting gaps and limitations in existing approaches, lexicons, and annotated datasets. The primary objective of this review is to assist researchers in identifying these gaps and limitations while offering accessible annotated datasets, preprocessing techniques, and procedures. We defined specific criteria for selecting research publications from the last 10 years, including 150 papers in our review process, while excluding earlier publications. The review utilized multiple databases, including Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science. The inherent complexity of the Arabic language, due to its unique traits and diverse dialects, presents significant challenges in ASA. Moreover, the lack of annotated datasets, lexicon resources, and programming tools further complicates sentiment analysis in Arabic. The morphological variations within Arabic make it linguistically challenging. To address these issues, it is crucial to develop additional resources and construct new Arabic sentiment lexicons that account for the various dialects within Modern Standard Arabic (MSA). Our findings reveal that there is no standard public lexicon that adequately enhances the calculation of ASA across different domains, such as e-commerce, politics, public health, and marketing.
Keywords: And lexical tools; Arabic sentiment analysis; Machine learning.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



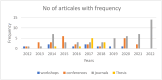

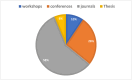


Similar articles
-
Using deep learning to analyze the psychological effects of COVID-19.Front Psychol. 2023 Aug 14;14:962854. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.962854. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37663328 Free PMC article.
-
ArabBert-LSTM: improving Arabic sentiment analysis based on transformer model and Long Short-Term Memory.Front Artif Intell. 2024 Jul 2;7:1408845. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1408845. eCollection 2024. Front Artif Intell. 2024. PMID: 39015364 Free PMC article.
-
Quantum computing and machine learning for Arabic language sentiment classification in social media.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 12;13(1):17305. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44113-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37828056 Free PMC article.
-
Fake news detection: state-of-the-art review and advances with attention to Arabic language aspects.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025 Mar 11;11:e2693. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2693. eCollection 2025. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025. PMID: 40134874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sentiment analysis of clinical narratives: A scoping review.J Biomed Inform. 2023 Apr;140:104336. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2023.104336. Epub 2023 Mar 22. J Biomed Inform. 2023. PMID: 36958461
Cited by
-
Prompt-based fine-tuning with multilingual transformers for language-independent sentiment analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20834. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03559-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pang B., Lee L. Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Foundations and Trends® in information retrieval. 2008;2(1–2):1–135.
-
- Abdulla N.A., Ahmed N.A., Shehab M.A., Al-Ayyoub M. 2013 IEEE Jordan Conference on Applied Electrical Engineering and Computing Technologies (AEECT) IEEE; 2013, December. Arabic sentiment analysis: lexicon-based and corpus-based; pp. 1–6.
-
- Farra N., Challita E., Abou Assi R., Hajj H. 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops. IEEE; 2010, December. Sentence-level and document-level sentiment mining for Arabic texts; pp. 1114–1119.
-
- Alwakid G., Osman T., Hughes-Roberts T. Challenges in sentiment analysis for Arabic social networks. Procedia Computer Science. 2017;117:89–100. .
-
- Jeong N., Lee J. An aspect-based review analysis using ChatGPT for the exploration of hotel service failures. Sustainability. 2024;16(4):1640. .
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

