Anti-inflammatory role of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-induced M1 polarization of RAW264.7 cells via Wnt2b/AXIN/β-catenin
- PMID: 39553710
- PMCID: PMC11568821
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.18448
Anti-inflammatory role of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-induced M1 polarization of RAW264.7 cells via Wnt2b/AXIN/β-catenin
Abstract
Background: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) is a special type of low-intensity ultrasound. In periodontal disease, LIPUS is applied as an adjuvant and non-invasive treatment. It has been reported that LIPUS significantly shifts the macrophage phenotype from M1 to M2, but the specific mechanism behind this shift is still unknown.
Methods: RAW264.7 cells were induced to M1/M2 polarization with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/interleukin-4 (IL4). LIPUS was performed for 25 min two times, 24 h apart, at an intensity of 45 mW/cm2 to stimulate RAW264.7 cells. PolyA mRNA sequencing was conducted of both the LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells and the LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells with LIPUS treatment. The expression of Wnt2b in RAW264.7 cells was downregulated by siRNA. The macrophage surface markers and downstream inflammatory cytokines were detected using flow cytometry. The relative expression of proteins in the Wnt2b/AXIN/β-catenin pathway was assessed using reverse transcription real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blot.
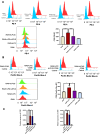
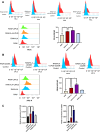
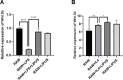
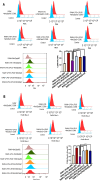
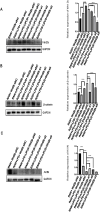
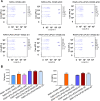
Results: LIPUS reversed the M1 polarization of RAW264.7 cells, with decreased expression of CD80 and CD86. In addition, LIPUS enhanced the M2 polarization of RAW264.7 cells, with upregulated expression of CD163 and CD206. The polyA mRNA sequencing results indicated that the Wnt signaling pathway participated in the M1 polarization of LIPUS-treated RAW264.7. The results of the RT-qPCR showed a higher expression of Wnt2b in LIPUS-treated and M1- or M2-polarized RAW264.7 cells. Knocking down Wnt2b was shown to reverse the inhibitory effect of LIPUS on M1 polarization and increase the expression of CD80 and CD86. Wnt2b knockdown also regulated downstream AXIN, β-catenin, and inflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) and interleukin-6 (IL6).
Conclusions: LIPUS plays an anti-inflammatory role by inhibiting LPS-induced M1 polarization of RAW264.7 cells in a Wnt2b/AXIN/β-catenin-dependent way. LIPUS may play a therapeutic role in periodontal diseases by inhibiting inflammation through the regulation of macrophage differentiation.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound; M1 polarization; Periodontal disease; WNT2b.
© 2024 Yin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

