This is a preprint.
Coordinated translational control of multiple immune checkpoints by the integrated stress response pathway in lung cancer
- PMID: 39554171
- PMCID: PMC11565990
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.10.23.619897
Coordinated translational control of multiple immune checkpoints by the integrated stress response pathway in lung cancer
Update in
-
The Integrated Stress Response Pathway Coordinates Translational Control of Multiple Immune Checkpoints in Lung Cancer.Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 15;85(14):2574-2590. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-3844. Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40327600 Free PMC article.
Abstract
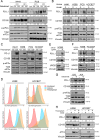
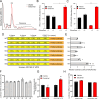
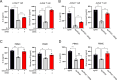
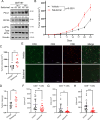
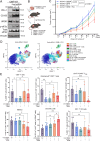
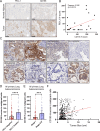
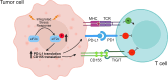
The integrated stress response (ISR) is an adaptive pathway hijacked by cancer cells to survive cellular stresses in the tumor microenvironment. ISR activation potently induces Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1), leading to suppression of anti-tumor immunity. Here we sought to uncover additional immune checkpoint proteins regulated by the ISR to elucidate mechanisms of tumor immune escape. We show that CD155 and PD-L1 are coordinately induced by the ISR, enhancing translation of both immune checkpoint proteins through bypass of inhibitory upstream open reading frames (uORFs) in their 5' UTRs. Analysis of primary human lung tumors identifies a significant correlation between PD-L1 and CD155 expression. ISR activation accelerates tumorigenesis and inhibits T cell function, effects that can be overcome by combining PD-1 blockade with the ISR inhibitor ISRIB. These studies uncover a novel mechanism by which two immune checkpoint proteins are coordinately regulated and suggest a new therapeutic strategy for lung cancer patients.
Statement of significance: This study uncovers a novel mechanism for the coordinated translational regulation of the PD-L1/PD1 and CD155/TIGIT immune checkpoint pathways and highlights the ISR as a therapeutic vulnerability for lung cancer. Inhibition of the ISR pathway bolsters PD-1 blockade, potentially unveiling a new therapeutic strategy for lung cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H, Hirano F, Flies DB, et al. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 2002;8(8):793–800. - PubMed
-
- Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH, et al. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature. 2006;439(7077):682–7. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
