Visual and Anatomic Responses in Patients With Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration and a Suboptimal Response to Anti-VEGF Therapy Switched to Faricimab
- PMID: 39554629
- PMCID: PMC11562232
- DOI: 10.1177/24741264241271649
Visual and Anatomic Responses in Patients With Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration and a Suboptimal Response to Anti-VEGF Therapy Switched to Faricimab
Abstract
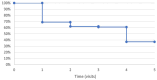
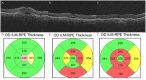
Purpose: To determine the efficacy of switching to intravitreal (IVT) faricimab in patients with treatment-resistant neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) and determine the rates of reversion to the original antivascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) therapy. Methods: A retrospective chart review was performed of patients with nAMD and persistent fluid on optical coherence tomography previously treated with anti-VEGF injections who received at least 1 IVT faricimab injection between March 1, 2022, and January 31, 2023. Results: The study comprised 135 eyes of 119 patients. Before switching to IVT faricimab, the mean number of anti-VEGF injections in the previous 12 months was 10.7 ± 2.6 (SD) with a mean interval of 4.8 ± 1.3 weeks (range, 2-8). The mean follow-up was 11.6 ± 2 months. Thirty eyes (22.2%) switched to IVT faricimab returned to the original therapy. Of the 105 eyes remaining on IVT faricimab, 66 (62.9%) had no fluid at the last follow-up. Compared with the original treatment, there was a significant improvement in logMAR visual acuity at the last follow-up in eyes on IVT faricimab (0.42 vs 0.38; P < .01) and in central subfield thickness (286 µm vs 246 µm; P < .0001). There was also a significant increase in the dosing interval after the third injection vs before IVT faricimab was prescribed (4.8 weeks vs 5.5 weeks; P < .001). Conclusions: Faricimab has a potent drying effect and potential for increasing the injection interval in many eyes with nAMD and persistent fluid on other anti-VEGF agents. Although nearly 25% of eyes reverted to the original therapy because of an insufficient response or adverse events, the majority did not achieve fluid resolution after reversion.
Keywords: aflibercept; bevacizumab; faricimab; neovascular age-related macular degeneration; vascular endothelial growth factor.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Heier, Shah, Cleary, Reed, Choi, and Nanda are sub-investigators in clinical trials sponsored by Genentech and Regeneron. Dr. Witkins is an investigator for Genentech. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Wong WL, Su X, Li X, et al. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(2):e106-e116. - PubMed
-
- Rubio RG, Adamis AP. Ocular angiogenesis: vascular endothelial growth factor and other factors. Dev Ophthalmol. 2016;55:28-37. - PubMed
-
- Rofagha S, Bhisitkul RB, Boyer DS, et al. Seven-year outcomes in ranibizumab-treated patients in ANCHOR, MARINA, and HORIZON: a multicenter cohort study (SEVEN-UP). Ophthalmology. 2013;120(11):2292-2299. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

