Gamma knife radiosurgery clinical efficacy for brain stem glioma: The institutional experience
- PMID: 39554666
- PMCID: PMC11568738
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.40.10.9658
Gamma knife radiosurgery clinical efficacy for brain stem glioma: The institutional experience
Abstract
Objective: In the past, brain stem was treated with surgery or placement of shunt in Pakistan. Gamma Knife surgery is currently an alternative to surgery for deep brain lesions. In the current study, we show the clinical experience of our Centre treated with Gamma Knife surgery.
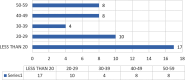
Methods: This is a descriptive study conducted between February 2016 and October 2021. We had total 47 patients presented with focal brainstem gliomas which were selected for Gamma knife radiosurgery at the Neurospinal and Cancer Care Institute Karachi.
Results: Clinical Response was observed among them 20 (42.55%) patients improved, 22(46.80%) were stable, while 05 (10.63%) got worse The mean duration of symptoms was 31.9(SD10.5± 3months). Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) scores during Gamma knife radiosurgery were 90 in 24 patients (51%), 80 in 21 patients (44.6%), and 70 in two patients (4.2%). Four patients (10.6%) had received conventional radiotherapy before Gamma knife radiosurgery.
Conclusion: Among the diverse gliomas, their peril varies not just by type but also by their intricate location within the brain. The efficacy of gamma knife radiation is excellent particularly when tackling high-grade tumors, exhibiting its prowess in both adult and pediatric cases.
Keywords: Brainstem glioma; Gamma Knife; Oncology; Radiosurgery; Stereotactic surgery.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
References
-
- Kuzan-Fischer CM, Souweidane MM. The intersect of neurosurgery with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma:JNSPG 75th Anniversary Invited Review Article. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2019;24(6):611–621. doi:10.3171/2019.5. PEDS18376. - PubMed
-
- Tanrıkulu B, Ozek MM. Clinical presentation and assessment for brainstem tumors. Brainstem Tumors:Diagnosis and Management. Springer. 2020:95–108. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-38774-7_4.
-
- Faulkner H, Arnaout O, Hoshide R, Young IM, Yeung JT, Sughrue ME, et al. The surgical resection of brainstem glioma:Outcomes and prognostic factors. World Neurosurg. 2021;146:e639–650. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2020.10.147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous