Design, Synthesis, Pharmacological Evaluation of Quinazolin-4(3 H)-Ones Bearing Urea Functionality as Potential VEGFR-2 Inhibitors
- PMID: 39554760
- PMCID: PMC11568772
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S490930
Design, Synthesis, Pharmacological Evaluation of Quinazolin-4(3 H)-Ones Bearing Urea Functionality as Potential VEGFR-2 Inhibitors
Abstract
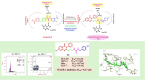
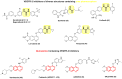
Background: In response to the urgent need for continuous discovery of new anti-proliferative agents, a new series of quinazoline compounds 5a-r was prepared.
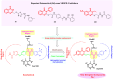
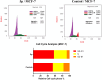
Methods: As a reference, four cancer cell lines-HCT116, HePG2, Hela, and MCF-7-and sorafenib (SOR) were used to assess the novel motifs' in vitro anticancer efficacy. The most cytotoxic compounds were tested in a VEGFR-2 suppressive test and flow cytometric test. Docking analysis was done to the three novel motifs.
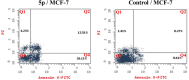
Results: Compound 5d showed the best anti-tumor activity of the tested compounds with IC50 6.09, 2.39, 8.94 and 4.81 μM in succession. In addition, compound 5h revealed a potent anticancer effect against HCT116 and HePG2 with IC50 5.89 and 6.74 μM, respectively. Also, compound 5p exhibited very strong activity against HCT116, HePG2 & MCF7 with IC50 8.32, 9.72 and 7.99, respectively. Compound 5p had the highest inhibition against VEGFR-2 with an IC50 of 0.117 μM, in contrast to 0.069 μM for SOR. According to flow cytometric testing, the most effective VEGFR-2 inhibitory agent, 5p, was shown to suppress the G1/S cell population in MCF-7 cells. Docking analysis confirmed that the three novel motifs could bind to the VEGFR-2 enzyme's binding region like the co-crystallized ligand SOR did.
Conclusion: The enzyme inhibitory test of compound 5p showed that it is the most potent hybrid that caused MCF-7 cells to undergo apoptosis and generated a G1/S cell cycle arrest. Confirmation of the obtained results was done with the aid of the docking study, which showed that the three motifs might adhere to the enzyme's major active sites, and the results were in good accordance with the experimental VEGFR-2 inhibitory results. We can conclude that the new quinazoline compounds 5a-r could be used as candidates for development of more efficient anticancer inhibitors.
Keywords: VEGFR-2 inhibitors; apoptosis; cell cycle analysis; molecular docking; quinazolines.
© 2024 Al-Sanea et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Hamdi A, Said E, Farahat AA, El-Bialy SAA, Massoud MAM. Synthesis and in vivo antifibrotic activity of novel leflunomide analogues. Lett Drug Des Discov. 2016;13(9):912–920. doi: 10.2174/1570180813666160630125624 - DOI
-
- Ali R, Mirza Z, Ashraf GM, et al. New anticancer agents: recent developments in tumor therapy. Anticancer Res. 2012;32(7):2999–3005. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

