Multi-omics association study integrating GWAS and pQTL data revealed MIP-1α as a potential drug target for erectile dysfunction
- PMID: 39555095
- PMCID: PMC11565697
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1495970
Multi-omics association study integrating GWAS and pQTL data revealed MIP-1α as a potential drug target for erectile dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Erectile dysfunction (ED) brings heavy burden to patients and society. Despite the availability of established therapies, existing medications have restricted efficacy. Therefore, we utilized a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) approach to find the drug targets that might enhance the clinical outcome of ED.
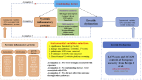
Methods: Genetic instruments associated with circulating inflammatory proteins were obtained from a genome-wide association study (GWAS) involving 8,293 European participants. Summary statistics for ED were extracted from a meta-analysis of the United Kingdom Biobank cohort compromised of 6,175 cases and 217,630 controls with European descent. We utilized multi-omics method and MR study to explore potential drug targets by integrating GWAS and protein quantity trait loci (pQTL) data. Inverse-variance weighted (IVW) method was applied as the primary approach. Cochran's Q statistics was employed to investigate the presence of heterogeneity. Furthermore, we identify the potential therapeutic drug targets for the treatment of ED utilizing molecular docking technology.
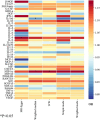
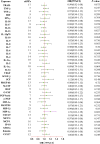
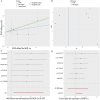
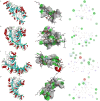
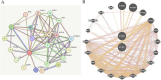
Results: This MR analysis of integrating GWAS and pQTL data showed that macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1α) was causally associated with the risk of ED (OR:1.19, 95%CI:1.02-1.39, p = 0.023). Meanwhile, the results of the weighted median model were consistent with the IVW estimates (OR:1.26, 95%CI:1.04-1.52, p = 0.018). Sensitivity analysis revealed no horizontal pleiotropy and heterogeneity. Furthermore, four anti-inflammatory or tonifying small molecular compounds, encompassing echinacea, pinoresinol diglucoside, hypericin, and icariin were identified through molecular docking technology.
Conclusion: This study identified MIP-1α as an underlying druggable gene and promising novel therapeutic target for ED, necessitating further investigation to detect the potential mechanisms by which MIP-1α might impact the development of ED.
Keywords: GWAS; MIP-1α; drug target; erectile dysfunction; multi-omics.
Copyright © 2024 Liu and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akintunde J. K., Olayinka M. C., Ugbaja V. C., Akinfenwa C. A., Akintola T. E., Akamo A. J., et al. (2023). Downregulation of inflammatory erectile dysfunction by Mantisa religiosa egg-cake through NO-cGMP-PKG dependent NF-kB signaling cascade activated by mixture of salt intake. Toxicol. Rep. 10, 633–646. 10.1016/j.toxrep.2023.05.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arana Rosainz Mde J., Ojeda M. O., Acosta J. R., Elias-Calles L. C., Gonzalez N. O., Herrera O. T., et al. (2011). Imbalanced low-grade inflammation and endothelial activation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and erectile dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 8, 2017–2030. 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02277.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

