Collateral susceptibility-guided alternation of ceftolozane/tazobactam with imipenem prevents resistance development in XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms
- PMID: 39555141
- PMCID: PMC11565044
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2024.100231
Collateral susceptibility-guided alternation of ceftolozane/tazobactam with imipenem prevents resistance development in XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms
Abstract
Objectives: New combinations of β-lactams and β-lactamase inhibitors, such as ceftolozane/tazobactam could be useful to combat biofilm-driven chronic infections by extensively resistant (XDR) Pseudomonas aeruginosa but resistance development by mutations in the Ω-loop of AmpC has been described. However, these mutations confer collateral susceptibility to carbapenems. Thus we aimed to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy and the prevention of resistance development of regimen alternating ceftolozane/tazobactam and imipenem.
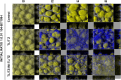
Methods: A carbapenem-resistant XDR P. aeruginosa clinical strain (ST175, 104-B7) and its isogenic imipenem-susceptible ceftolozane/tazobactam-resistant mutant derivative (AmpC T96I, 104-I9) were used. Experiments of single strains and mixed (104-B7 and 104-I9, 1:0.01 ratio) biofilms were performed. 48h biofilms (flow cell system) were treated for 6 days with either ceftolozane/tazobactam, 4/4 mg/L or the alternation of ceftolozane/tazobactam (2 days)-imipenem 4 mg/L (2 days) - ceftolozane/tazobactam (2 days). After treatment, biofilms were collected and plated on Mueller-Hinton agar± ceftolozane/tazobactam 4/4 mg/L. Structural dynamics were monitored using confocal laser scanning microscopy and images were processed with IMARIS software. At least, three independent triplicate experiments per condition were performed. Emerging resistant mutants were characterized through whole genome sequencing (Illumina).
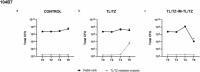
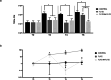
Results: Ceftolozane/tazobactam monotherapy failed to reduce the biofilms of the 104-B7 XDR strain and led to the selection of resistant mutants that showed AmpC Ω-loop mutations (T96I, L244R or aa236Δ7). On the contrary, alternation with imipenem enhanced activity (3 Logs reduction at day 6) and prevented the emergence of ceftolozane/tazobactam-resistant mutants. Likewise, treatment with ceftolozane/tazobactam dramatically amplified the resistant strain 104-I9 in mixed biofilms (>90 % of the population), while the alternation regimen counterselected it.
Conclusions: Collateral susceptibility-guided alternation of ceftolozane/tazobactam with imipenem effectively prevented the selection of resistant mutants and thus could be a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of P. aeruginosa XDR chronic infections.
Keywords: Antagonistic resistance mechanisms to antibiotics; Biofilms; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; XDR.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Kragh K.N., Richter K. Antibiofilm strategies: current and future applications to prevent, control and eradicate biofilms. Springer International Publishing; Cham: 2022. Introduction: biofilms 101; pp. 3–15.
-
- Costerton J.W., et al. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999;284:1318–1322. - PubMed
-
- Høiby N., Bjarnsholt T., Moser C., Bassi G.L., Coenye T., Donelli G., Hall-Stoodley L., Holá V., Imbert C., Kirketerp-Møller K., Lebeaux D., Oliver A., Ullmann A.J., Williams C., ESCMID Study Group for Biofilms and Consulting External Expert Werner Zimmerli ESCMID guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of biofilm infections 2014. Clin Microbiol Infection: the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 2015;21(Suppl 1):S1–S25. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2014.10.024. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

