Effects of Different Astaxanthin Sources on Fillet Coloration and Energy Deposition in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
- PMID: 39555536
- PMCID: PMC10984719
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/1664203
Effects of Different Astaxanthin Sources on Fillet Coloration and Energy Deposition in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Abstract
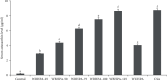
A 9-week feeding trial was conducted to investigate the effects of different dietary sources of astaxanthin on fillet coloration, texture, and nutrient composition in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Eight diets were formulated to contain 0, 25, 50, 75, 100, and 125 mg/kg astaxanthin from wall-broken Haematococcus pluvialis (WBHPA), 100 mg/kg astaxanthin from wall-unbroken H. pluvialis (WUHPA), or chemically synthesized astaxanthin (CSA). Each diet was fed to triplicate groups of rainbow trout (mean initial weight of 561 g) twice daily (07:00 and 17:00) to apparent satiation for 9 weeks. Results showed that at the 100 mg/kg astaxanthin inclusion level, the CAS group had higher fillet gross energy, dorsal fillet redness, and dorsal fillet color card score compared to the WBHPA-100 group, with both being higher than the WUHPA group (P < 0.05). Fillet astaxanthin content, dorsal fillet yellowness, and lateral line redness and yellowness did not differ significantly between the CSA and WBHPA-100 groups (P > 0.05), but were higher than the WUHPA group. When WBHPA was used, the inclusion of 50-100 mg/kg decreased fillet lightness but increased fillet redness, while better fillet texture was served at 75-125 mg/kg. Dietary 25-125 mg/kg WBHPA inclusion increased fillet astaxanthin and gross energy concentrations, with minor effects on fatty acid compositions of fillet. Inclusion of over 100 mg/kg astaxanthin regardless of source decreased fillet threonine and serine contents, and the WBHPA-100 group had lower fillet glycine and alanine contents compared to the control group (P < 0.05). In conclusion, CSA had the most significant impact on fillet coloration and energy deposition in rainbow trout, while WUHPA had the least favorable effect. Additionally, the wall-breaking treatment of H. pluvialis can improve the effect of astaxanthin on fillet coloration and nutrient composition in rainbow trout, with a recommended dose range of 75-100 mg/kg.
Copyright © 2024 Xiaoxue Meng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture, Towards Blue Transformation . Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; 2022.
-
- Booth M. A., Warner-Smith R. J., Allan G. L., Glencross B. D. Effects of dietary astaxanthin source and light manipulation on the skin colour of Australian snapper Pagrus auratus (Bloch & Schneider, 1801) Aquaculture Research . 2004;35(5):458–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.2004.01038.x. - DOI
-
- Pan C.-H., Chien Y.-H. Effects of dietary supplementation of alga Haematococcus pluvialis (flotow), synthetic astaxanthin and β-carotene on survival, growth, and pigment distribution of red devil, Cichlasoma citrinellum (Gunther) Aquaculture Research . 2009;40(8):871–879. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.02153.x. - DOI
-
- Zhang J., Li X., Leng X., Zhang C., Han Z., Zhang F. Effects of dietary astaxanthins on pigmentation of flesh and tissue antioxidation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Aquaculture International . 2013;21(3):579–589. doi: 10.1007/s10499-012-9590-9. - DOI
-
- Pham M. A., Byun H.-G., Kim K.-D., Lee S.-M. Effects of dietary carotenoid source and level on growth, skin pigmentation, antioxidant activity and chemical composition of juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture . 2014;431:65–72. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.04.019. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources