Introducing a Novel Pacemaker-Mediated Arrhythmia: The Pseudo-RNRVAS Arising From Atrial Capture Challenges
- PMID: 39555895
- PMCID: PMC11571235
- DOI: 10.1111/anec.70033
Introducing a Novel Pacemaker-Mediated Arrhythmia: The Pseudo-RNRVAS Arising From Atrial Capture Challenges
Abstract
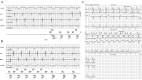
Background: This study aimed to define and explain a novel form of pacemaker-mediated arrhythmia which is initiated and sustained by atrial capture loss coinciding with ventriculoatrial (VA) conduction within the postventricular atrial refractory period (PVARP). Unlike repetitive nonreentrant VA synchrony (RNRVAS), in the pseudo-RNRVAS, the atrium is not stimulated due to pacing below the threshold level, rather than because of refractory atrial myocardium.
Objective: The objective was to elucidate the mechanisms of this pseudo-RNRVAS, identify predisposing factors, and propose preventive strategies.
Methods: Twenty-one patients with dual-chamber cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) exhibiting stable VA conduction within the PVARP were included. Pseudo-RNRVAS were induced by altering atrial amplitude and lower rate interval while keeping other CIED parameters constant.
Results: Pseudo-RNRVAS developed after atrial capture loss in 20 out of 21 patients. Notably, 11 patients experienced pseudo-RNRVAS at heart rates ≤ 70 bpm, and 7 patients at AV delay ≤ 150 ms. The condition initiated immediately following the first ventricular pace beat after atrial capture loss in 18 patients. In six cases, pseudo-RNRVAS terminated intermittently and then restarted; in 14 cases, it did not resolve.
Conclusion: Pseudo-RNRVAS can occur even at low heart rates and without specific predisposing factors seen in RNRVAS. Conditions that increase atrial pacing probability and threshold raise the likelihood of pseudo-RNRVAS. Early postimplantation may pose a heightened risk, correlating with pacemaker syndrome and susceptibility to heart failure.
Keywords: RNRVAS; endless loop tachycardia; loss of atrial capture; pacemaker‐mediated arrhythmia; pacemaker‐mediated tachycardias; pseudo‐RNRVAScardiac implantable electronic device; repetitive nonreentrant ventriculoatrial synchrony.
© 2024 The Author(s). Annals of Noninvasive Electrocardiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Barold, S. S. 2017. “A Review of the Atrial Upper Rate Algorithms of St. Jude Medical (Abbott) Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: Incidence of Repetitive Nonreentrant Ventriculoatrial Synchrony (RNRVAS).” Herzschrittmachertherapie & Elektrophysiologie 28: 320–327. 10.1007/s00399-017-0517-z. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

