Association between periodontitis and cardiometabolic index (CMI): a study from NHANES 2009-2014
- PMID: 39557890
- PMCID: PMC11574172
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78382-7
Association between periodontitis and cardiometabolic index (CMI): a study from NHANES 2009-2014
Abstract
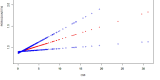
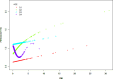
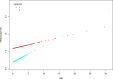
Cardiometabolic index (CMI) is a novel anthropometric metric that integrates lipid and adiposity characteristics. The correlation between periodontitis development and CMI is ambiguous. The objective of this study was to establish the association between CMI and periodontitis by analyzing data from the NHANES (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey) database. A cross-sectional study was conducted on a cohort of 6188 people selected from the NHANES database, covering the period from 2009 to 2014. The study employed multivariate logistic regression to examine the independent correlation between CMI and periodontitis. Subgroup data were analyzed and interaction tests were conducted to assess the impact of variables on the correlation between CMI and periodontitis. The CMI index was significantly and positively associated with the presence of periodontitis (β = 0.03, 95%CI(0.01, 0.05), p = 0.0092). In addition, a U-shaped relationship was found between CMI index and periodontitis severity in an older American population (65 < = age < = 80, with a folding point of 1.44, p = 0.008). This study demonstrates a significant correlation between CMI and periodontitis, positioning CMI as a crucial indicator for assessing periodontal health. Future efforts should prioritize oral hygiene interventions for patients with elevated CMI levels to facilitate early intervention and enhance overall health outcomes.
Keywords: Cardiometabolic index (CMI); Cross-sectional study; NHANES; Periodontitis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between cardiometabolic index (CMI) and periodontitis in US adults: analysis of NHANES data (2009-2014).BMC Oral Health. 2024 Nov 6;24(1):1346. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-05119-3. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39506722 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Cardiometabolic index and endometriosis in a US nationally representative sample: results from NHANES 1999-2006.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 12;15:1450965. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1450965. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39600949 Free PMC article.
-
Association of cardiometabolic index with sleep quality in adults: a population‑based study.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 29;14(1):26019. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77855-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39472685 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between cardiometabolic index and female infertility: a cross-sectional analysis.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024 Nov 14;22(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01312-9. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39543672 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between cardiometabolic index and infertility in American adults: a population-based study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 4;15:1424033. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1424033. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39296717 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Baseline and changes in cardiometabolic index and incident cardiovascular disease in two prospective cohorts.Am J Prev Cardiol. 2025 Jun 17;23:101046. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpc.2025.101046. eCollection 2025 Sep. Am J Prev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40612280 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin-Loaded Thermoresponsive Hydrogel as a Potential Drug Delivery System for Periodontal Disease in a Rat Model of Ligature-Induced Periodontitis.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jul 31;17(15):2108. doi: 10.3390/polym17152108. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40808155 Free PMC article.
-
Association between visceral adiposity index and oral health status in a National survey.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 28;15(1):27486. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11803-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40721428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Linden, G. J., Lyons, A. & Scannapieco, F. A. Periodontal systemic associations: Review of the evidence. J. Clin. Periodontol. 40 (Suppl 14), S8–19 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

