Mathematical analysis with control of liver cirrhosis causing from HBV by taking early detection measures and chemotherapy treatment
- PMID: 39557923
- PMCID: PMC11574201
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79597-4
Mathematical analysis with control of liver cirrhosis causing from HBV by taking early detection measures and chemotherapy treatment
Abstract
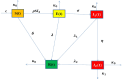
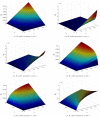
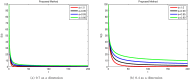
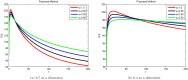
Reformulating the physical processes associated with the evolution of different ailments in accordance with globally shared objectives is crucial for deeper comprehension. This study aims to investigate the mechanism by which the HB virus induces harmful inflammation of the liver, with a focus on early detection and therapy using corticosteroids or chemotherapy. Based on the developed hypothesis, a new mathematical model has been created for this purpose. The recently developed system for HBV is , which is examined both quantitatively and qualitatively to determine its actual effect on stability. Reliable conclusions are ensured by examining the system's boundedness, positivity, existence, uniqueness, and conducting local and global stability analysis-all crucial components of epidemic models. Global stability is tested using Lyapunov first derivative functions to assess the overall impact of asymptomatic persons and chemotherapy treatment. Additionally, the Lipschitz condition is used to confirm the unique solutions for the newly built HBV model using methods from fixed point theory, thus meeting the requirements for uniqueness and existence. Since the population must maintain this property, positivity is confirmed using global derivatives and Lipschitz criteria to calculate the rate of change in each sub-compartment. Applying the Mittag-Leffler kernel with a fractal-fractional operator to continuously monitor the HBV virus for liver cirrhosis infection yields dependable results. Furthermore, the current situation regarding the HBV outbreak pertaining to liver cirrhosis infection, along with the control measures implemented following early diagnosis through asymptomatic measures and chemotherapy treatment under constant observation, are established to prevent chronic stage infections. Simulations have been used to study the true behavior and impact of HBV in asymptomatic persons receiving chemotherapy for liver cirrhosis infection in the community. This research is essential for understanding the spread of viruses and developing control strategies based on our validated findings to mitigate the risk factors associated with liver cirrhosis.
Keywords: Asymptomatic measures; Hepatitis B model; Liver cirrhosis; Mittag-Leffler kernel; Positive invariant region.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
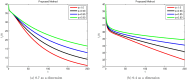
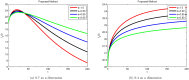
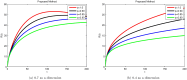
References
-
- WHO. Hepatitis B Fact Sheet No. 204 (The World Health Organisation, 2013). http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs204/en/.
-
- Zada, I. et al. Mathematical analysis of hepatitis B epidemic model with optimal control. Adv. Differ. Equ.2021, 1–29 (2021).
-
- World Health Organization. Unsafe Injection Practices Having Serious Large-Scale Consequences. Press Release WHO/14 (2000).
-
- Mariano, A. et al. Role of beauty treatment in the spread of parenterally transmitted hepatitis viruses in Italy. J. Med. Virol.74(2), 216–220 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Favero, M. S. & Bolyard, E. A. Microbiologic considerations: Disinfection and sterilization strategies and the potential for airborne transmission of bloodborne pathogens. Surg. Clin. N. Am.75(6), 1071–1089 (1995). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

