Intrinsically disordered RNA-binding motifs cooperate to catalyze RNA folding and drive phase separation
- PMID: 39558160
- PMCID: PMC11662656
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1107
Intrinsically disordered RNA-binding motifs cooperate to catalyze RNA folding and drive phase separation
Abstract
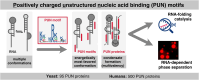
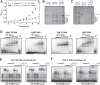
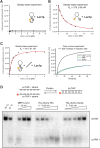
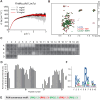
RNA-binding proteins are essential for gene regulation and the spatial organization of cells. Here, we report that the yeast ribosome biogenesis factor Loc1p is an intrinsically disordered RNA-binding protein with eight repeating positively charged, unstructured nucleic acid binding (PUN) motifs. While a single of these previously undefined motifs stabilizes folded RNAs, multiple copies strongly cooperate to catalyze RNA folding. In the presence of RNA, these multivalent PUN motifs drive phase separation. Proteome-wide searches in pro- and eukaryotes for proteins with similar arrays of PUN motifs reveal a strong enrichment in RNA-mediated processes and DNA remodeling. Thus, PUN motifs are potentially involved in a large variety of RNA- and DNA-related processes by concentrating them in membraneless organelles. The general function and wide distribution of PUN motifs across species suggest that in an ancient 'RNA world' PUN-like motifs may have supported the correct folding of early ribozymes.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
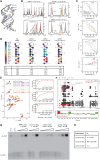
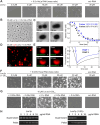
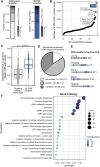

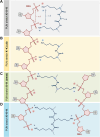
References
-
- Kressler D., Hurt E., Bassler J.. Driving ribosome assembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010; 1803:673–683. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

