Interaction of proteinuria and diabetes on the risk of cardiovascular events: a prospective cohort CKD-ROUTE study
- PMID: 39558295
- PMCID: PMC11572061
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-20715-2
Interaction of proteinuria and diabetes on the risk of cardiovascular events: a prospective cohort CKD-ROUTE study
Abstract
Objective: We evaluated the interaction of urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) with diabetes on the risk of cardiovascular events in a cohort study.
Methods: The study population consisted of 639 participants with chronic kidney disease (CKD) stages 2-5, enrolled between 2010 and 2011 in Japan. Cox proportional hazards models were used to evaluate the independent and combined effects of the UPCR and diabetes on cardiovascular events.
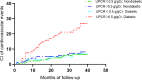
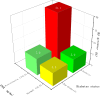
Results: During a median follow-up of 3 years, 59 participants developed cardiovascular events during follow-up. A notably higher risk of cardiovascular events was found in participants with proteinuria [hazards ratio (HR): 2.16, 95% confidence interval (95% CI): 1.17-3.97] compared to those without proteinuria at UPCR levels. In addition, the participants with diabetes had a higher risk of cardiovascular events (HR: 2.53, 95% CI: 1.49-4.30) than those without diabetes. Moreover, an interaction was found between UPCR and diabetes on cardiovascular events (P for interaction = 0.04). Participants with both proteinuria (UPCR ≥ 0.5 g/gCr) and diabetes had a 4.09 times higher risk of cardiovascular events (HR: 4.09, 95% CI: 1.97-8.47) compared with those without proteinuria (UPCR < 0.5 g/gCr) and diabetes.
Conclusions: In summary, among participants with CKD stages 2-5, proteinuria and diabetes were found to independently and jointly affect the risk of cardiovascular events. Participants with proteinuria and diabetes had the highest risk of cardiovascular events compared with other groups.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Chronic kidney disease; Diabetes; Proteinuria; Urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

