Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Blantyre, Malawi
- PMID: 39559263
- PMCID: PMC11572489
- DOI: 10.1099/acmi.0.000885.v3
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Blantyre, Malawi
Abstract
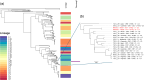
We announce the deposition of the first two enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) genomes from Malawi. They were isolated from the faeces of asymptomatically infected children obtained in 2014. Both genomes encode the porcine variant of the heat-labile toxin and no known ETEC colonization factors.
Keywords: E. coli; diarrhoea; genomics.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Troeger C, Blacker BF, Khalil IA, Rao PC, Cao S, et al. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoea in 195 countries: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Infecti Dis. 2018;18:1211–1228. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30362-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
