Evaluating the efficacy of curcumin in the management of oral potentially malignant disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39559334
- PMCID: PMC11572357
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.18492
Evaluating the efficacy of curcumin in the management of oral potentially malignant disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Oral potentially malignant disorders (OPMDs) not only harbour the risk of malignant transformation but can also affect patients' quality of life owing to severe symptoms. Therefore, there is an urgent need for therapeutic strategies to improve patients' quality of life. The objective of this meta-analysis was to comprehensively assess the efficacy of curcumin in the management of OPMDs.
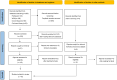
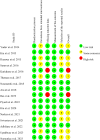
Methods: PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science were searched for clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of curcumin in the treatment of OPMDs from inception until March 2024. RevMan 5.4 software was used to perform statistical and subgroup analyses.
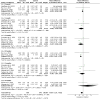
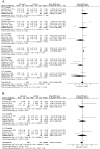
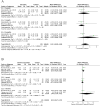
Results: Sixteen randomised controlled trials (1,089 patients) were selected. Curcumin exhibited comparable efficacy to conventional controls in alleviating pain (I2 = 98%, P = 0.49) and improving tongue protrusion (I2 = 94%, P = 0.51) in oral submucous fibrosis (OSF). Additionally, topical use of curcumin had an efficacy equivalent to that of conventional therapy in reducing pain (I2 = 83%, P = 0.31) and facilitating clinical remission (I2 = 67%, P = 0.38) of oral lichen planus (OLP).
Conclusion: The topical use of curcumin may palliate pain and promote clinical healing in OLP patients. Systemic curcumin can ameliorate the degree of pain and tongue protrusion in OSF. Therefore, our study suggests that curcumin could serve as an alternative treatment for managing OPMDs with lower medical toxicity than steroids, especially when steroids are not suitable. Further studies with larger sample sizes and adequate follow-up periods are required to validate our results.
Keywords: Curcumin; Oral lichen planus; Oral potentially malignant disorders; Oral submucous fibrosis; Systematic review.
© 2024 Shi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Fenugreek as an Adjuvant in the Management of Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2024 Oct 1;25(10):921-929. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3773. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2024. PMID: 39873252 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of curcumin for management of oral submucous fibrosis: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2019 Apr;127(4):300-308. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2019.01.010. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30745280
-
Possible action mechanism for curcumin in pre-cancerous lesions based on serum and salivary markers of oxidative stress.J Oral Sci. 2010 Jun;52(2):251-6. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.52.251. J Oral Sci. 2010. PMID: 20587949
-
Clinical safety and efficacy of curcumin use for oral lichen planus: a systematic review.J Dermatolog Treat. 2019 Sep;30(6):605-611. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2018.1543849. Epub 2018 Nov 28. J Dermatolog Treat. 2019. PMID: 30388912
-
Turmeric in the management of oral submucous fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cancer Res Ther. 2021 Apr-Jun;17(2):327-335. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_95_20. J Cancer Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34121673
Cited by
-
Elucidating the role of lipid metabolism dysregulation in the transition from oral lichen planus to oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2025 Apr 16;23(1):448. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06431-4. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40241125 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Experimental Anti-Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 3;26(13):6407. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136407. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adhikari S, Rimal J, Maharjan I, Shrestha A. Efficacy of curcumin in combination with intralesional dexamethasone with hyaluronidase in the treatment of oral submucous fibrosis: a randomized controlled trial. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention. 2022;23(9):3125–3132. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.9.3125. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ara SA, Mudda J, Lingappa A, Rao P, Zakaullah S. Efficacy of curcumin in oral submucous fibrosis-a randomized controlled clinical trial. Indian Journal of Dental Research. 2018;9(12):5277–5286. doi: 10.4103/ijdr.ijdr_551_16. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

