Research on the evaluation of emergency management capability for urban public health emergencies under the perspective of resilience-a case study of Henan Province, China
- PMID: 39559375
- PMCID: PMC11571321
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1431158
Research on the evaluation of emergency management capability for urban public health emergencies under the perspective of resilience-a case study of Henan Province, China
Abstract
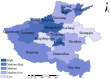
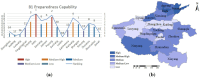
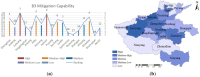
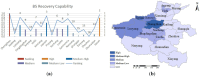
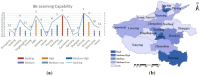
With the rapid development of the economy and society, the likelihood of sudden public health emergencies in urban areas continues to rise. In particular, major infectious diseases that have gained global attention, such as the SARS virus, H1N1 influenza, Ebola outbreak, and COVID-19 pandemic, have presented significant challenges to urban emergency management systems. Evaluating emergency management capability is a fundamental requirement for developing emergency response capacity. To this end, this study combines the theory of resilience with the theory of full-process equilibrium emergency management, selects 31 evaluation indicators from six key aspects: preparedness, forewarning, mitigation, disposal, recovery, and learning. The indicator weights are determined using the AHP-Entropy Weight Method, and a TOPSIS model is constructed to assess the emergency management capability of urban public health emergencies. The model's applicability is validated by examining 18 cities in Henan Province. The findings suggest that Jiaozuo, Hebi, Zhengzhou, and Luohe possess relatively robust emergency management capabilities for sudden public health incidents, whereas Kaifeng, Pingdingshan, and Shangqiu exhibit weaker capabilities.
Keywords: TOPSIS model; capacity evaluation; emergency management capacity; public health emergencies; the full process balance of emergency management.
Copyright © 2024 Hao, Tie, Zhang, Zhang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Xinhuanet. (2020). Xi Jinping: Speech at the national recognition meeting for the fight against Covid-19. Available at: http://www.xinhuanet.com/politics/2020-10/15/c_1126614978.htm (Accessed October 15,2020).
-
- Guo YS. Capacity of national civil servants to respond to emergencies. Beijing: China Social Sciences Press; (2005).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

