Supra-ceramics: a molecule-driven frontier of inorganic materials
- PMID: 39559526
- PMCID: PMC11571738
- DOI: 10.1080/14686996.2024.2416384
Supra-ceramics: a molecule-driven frontier of inorganic materials
Abstract
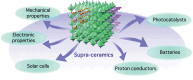
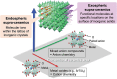
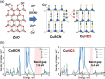
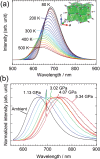
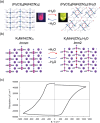
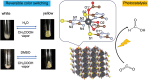
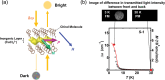
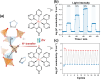
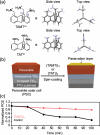
Discoveries and technological innovations over the past decade are transforming our understanding of the properties of ceramics, such as 'hard', 'brittle', and 'homogeneous'. For example, inorganic crystals containing molecular anions exhibit excellent secondary battery characteristics, and the fusion of inorganic solids and molecules results in innovative catalytic functions and physical properties. Different from the conventional ceramics such as metal oxides that are formed by monatomic cations and anions, unique properties and functions can be expected in molecular-incorporated inorganic solids, due to the asymmetric and dynamic properties brought about by the constituent molecular units. We name the molecular-incorporated inorganic materials that produce innovative properties and functions as supra-ceramics. In this article, we describe various kinds of supra-ceramics from the viewpoint of synthesis, analysis and physical properties/functions for a wide range of applications.
Keywords: CO2 conversion; Metal complexes; batteries; coordination polymers; metal-organic frameworks; organic-inorganic hybrids; perovskites; photocatalysts; proton conductors; solar cells.
Plain language summary
Recent discoveries/innovations are transforming ceramics by integrating molecular units, leading to new properties like enhanced battery performance and catalytic functions. Supra-ceramics, combining molecules and solids, promise innovative materials development.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by National Institute for Materials Science in partnership with Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures












References
-
- West AR. Solid state chemistry and its applications. UK: Wiley; 2014.
-
- Maeda K, Takeiri F, Kobayashi G, et al. Recent progress on mixed-anion materials for energy applications. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 2022;95(1):26–28. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.20210351 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
