Insights in AAV-mediated antigen-specific immunity and a strategy for AAV vaccine dose reduction through AAV-extracellular vesicle association
- PMID: 39559560
- PMCID: PMC11570487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101358
Insights in AAV-mediated antigen-specific immunity and a strategy for AAV vaccine dose reduction through AAV-extracellular vesicle association
Abstract
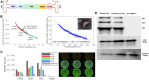
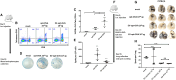
We previously showed therapeutic advantages of using a capsid-modified and encoded antigen-optimized AAV-based cancer vaccine to initiate strong antigen-specific immune responses and increase survival in a syngeneic mouse model of melanoma. In this study, we further explore AAV vaccine dose reduction and possible mechanisms of the immune response. Immunization with extracellular vesicle (EV)-associated AAV6-S663V encoded ovalbumin (OVA) or tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TRP-1) induced significantly higher levels of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells compared with standard AAV in mice. Importantly, a higher number of specific CD8+ T cells was achieved with EV-AAV several logs lower than optAAV-based doses. EV-optAAV-OVA was used in a dose 100 times lower, and EV-optTRP-1 10 times lower than optOVA and optTRP-1 correspondingly. Our data suggest that significant dose reduction for optimized AAV-based vaccines is possible without sacrificing efficiency. In addition, we studied the role of conventional type 1 dendritic cells (cDC1) in optimized AAV-based immunization using a C57BL/6-Irf8em1Kmm (Irf8 + 32-/-) mouse model lacking cDC1. Interestingly, we found that cDC1 are not essential for conveying effector T cell responses to AAV-encoded tumor antigens.
Keywords: adeno-associated virus; antigen-specific T cell; cancer vaccine; dendritic cell; extracellular vesicles; protective immune response.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.A. and K.K. have several issued or provisional patents related to AAV vectors that have been licensed to various gene therapy companies.
Figures



References
-
- Zakeri S.E., Pradeep S.P., Kasina V., Laddha A.P., Manautou J.E., Bahal R. Casimersen for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022;43:607–608. - PubMed
-
- Philippidis A. BioMarin's ROCTAVIAN Wins Food and Drug Administration Approval As First Gene Therapy for Severe Hemophilia A. Hum. Gene Ther. 2023;34:665–668. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

