Efficacy of Sacubitril/Valsartan in a Patient With Heart Failure and Impaired Secretion of Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Due to Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 39559600
- PMCID: PMC11571103
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.71844
Efficacy of Sacubitril/Valsartan in a Patient With Heart Failure and Impaired Secretion of Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Due to Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
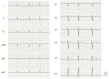
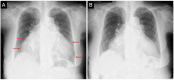
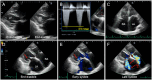
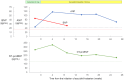
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is a circulating hormone released from the atria in response to wall stretch and volume overload in the setting of heart failure. When atrial fibrillation (AF) becomes long-standing persistent, ANP secretion in response to volume overload is impaired due to degenerative changes of the atria. Here, we report a case of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and impaired ANP secretion due to long-standing AF. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level was elevated (269 pg/mL), whereas the increase in ANP level was marginal (46.1 pg/mL), suggesting impaired ANP secretion due to long-standing AF. Valsartan (80 mg/day) was replaced with sacubitril/valsartan (100 mg/day) without changing other medications. Administration of sacubitril/valsartan was effective in improving the patient's symptoms, such as dyspnea and edema, and reducing NT-proBNP level by increasing endogenous ANP level from 46.1 pg/mL to 117 pg/mL in the first four weeks. This case highlights the possibility of impaired ANP secretion in response to volume overload as a predictor of the diuretic effect of sacubitril/valsartan in heart failure. This may lead to individualized treatment for each patient with heart failure based on natriuretic peptide profiles.
Keywords: echocardiography; electrocardiogram; mitral regurgitation; neprilysin; volume overload.
Copyright © 2024, Kurisu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Atrial fibrillation and risk of adverse outcomes in heart failure with reduced, mildly reduced, and preserved ejection fraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kroshian G, Joseph J, Kinlay S, Peralta AO, Hoffmeister PS, Singh JP, Yuyun MF. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2024;35:715–726. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
