A Combinatorial Functional Precision Medicine Platform for Rapid Therapeutic Response Prediction in AML
- PMID: 39560206
- PMCID: PMC11574777
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.70401
A Combinatorial Functional Precision Medicine Platform for Rapid Therapeutic Response Prediction in AML
Abstract
Background: Despite advances made in targeted biomarker-based therapy for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) treatment, remission is often short and followed by relapse and acquired resistance. Functional precision medicine (FPM) efforts have been shown to improve therapy selection guidance by incorporating comprehensive biological data to tailor individual treatment. However, effectively managing complex biological data, while also ensuring rapid conversion of actionable insights into clinical utility remains challenging.
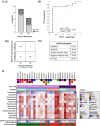
Methods: We have evaluated the clinical applicability of quadratic phenotypic optimization platform (QPOP), to predict clinical response to combination therapies in AML and reveal patient-centric insights into combination therapy sensitivities. In this prospective study, 51 primary samples from newly diagnosed (ND) or refractory/relapsed (R/R) AML patients were evaluated by QPOP following ex vivo drug testing.
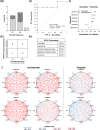
Results: Individualized drug sensitivity reports were generated in 55/63 (87.3%) patient samples with a median turnaround time of 5 (4-10) days from sample collection to report generation. To evaluate clinical feasibility, QPOP-predicted response was compared to clinical treatment outcomes and indicated concordant results with 83.3% sensitivity and 90.9% specificity and an overall 86.2% accuracy. Serial QPOP analysis in a FLT3-mutant patient sample indicated decreased FLT3 inhibitor (FLT3i) sensitivity, which is concordant with increasing FLT3 allelic burden and drug resistance development. Forkhead box M1 (FOXM1)-AKT signaling was subsequently identified to contribute to resistance to FLT3i.
Conclusion: Overall, this study demonstrates the feasibility of applying QPOP as a functional combinatorial precision medicine platform to predict therapeutic sensitivities in AML and provides the basis for prospective clinical trials evaluating ex vivo-guided combination therapy.
Keywords: AML; FLT3; combinatorial drug sensitivity; functional precision medicine.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
M.O. received honoraria from Jenssen, Novartis, Astellas, AbbVie, Pfizer Amgen, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb. E.K.H.C. is a shareholder of KYAN Technologies.
Figures




Similar articles
-
FLT3 mutated acute myeloid leukemia: 2021 treatment algorithm.Blood Cancer J. 2021 May 27;11(5):104. doi: 10.1038/s41408-021-00495-3. Blood Cancer J. 2021. PMID: 34045454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upfront intensive treatment analysis of the Italian Cohort Study on FLT3-mutated AML patients (FLAM): The impact of a FLT3 inhibitor addition to standard chemotherapy in the real-life setting.Cancer. 2025 Apr 1;131(7):e35824. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35824. Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40159434 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes with sequential FLT3-inhibitor-based therapies in patients with AML.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Oct 8;13(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00964-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33032648 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1 contributes to treatment failure in acute myeloid leukemia.JCI Insight. 2018 Aug 9;3(15):e121583. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.121583. eCollection 2018 Aug 9. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 30089730 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of FLT3 mutational analysis in acute myeloid leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2018 Oct;59(10):2273-2286. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1399312. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018. PMID: 29164965 Review.
Cited by
-
The interaction between common genetic mutations in AML and the immune landscape: mechanisms and implications for immune response.Front Immunol. 2025 Aug 11;16:1635111. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1635111. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40861464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

