Biocatalytic sulfation of aromatic and aliphatic alcohols catalyzed by arylsulfate sulfotransferases
- PMID: 39560778
- PMCID: PMC11576661
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-024-13354-5
Biocatalytic sulfation of aromatic and aliphatic alcohols catalyzed by arylsulfate sulfotransferases
Abstract
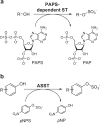
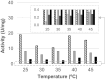
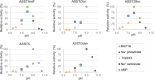
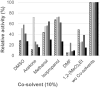
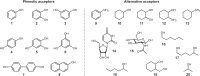
Many relevant metabolites, as well as chemical commodities, contain at least one sulfate ester group. Consequently, biocatalytic strategies to attach sulfate to a molecule under mild conditions are of high interest. In order to expand the enzymatic toolbox available, five new arylsulfate sulfotransferases (ASSTs) were identified in this study. Overexpression in Escherichia coli and enzyme purification resulted in soluble proteins which catalyzed the sulfate transfer to an acceptor substrate using p-nitrophenyl sulfate (pNPS) as sulfate donor. Optimal reaction conditions were established with respect to temperature and pH, as well as their tolerance to organic co-solvents and melting temperature. Additionally, the kinetic parameters (Vmax, KM, and kcat) were determined. The substrate scope for the acceptor showed that a structurally diverse spectrum of alcohols is accepted. The substrates included phenolic alcohols with one, two, and three hydroxy groups, linear and cyclic aliphatic alcohols, and amines. The phenolic substrates were accepted reaching activities of up to 154 U/mg purified enzyme. Additionally, also the aliphatic alcohols (both linear and cyclic) were accepted at reduced activity, showing that these enzymes are not limited to phenolic alcohols. Moreover, catalytic activity was detected when using aniline as an acceptor substrate implying their ability to sulfate also amino groups. Finally, the consecutive sulfation of di- and trihydroxy compounds was observed, resulting in the detection of the corresponding disulfated molecules. KEY POINTS: • Five novel arylsulfate sulfotransferases were identified and characterized. • Accepted substrates included aromatic and aliphatic alcohols, as well as aniline. • Disulfation of di- and trihydroxy aromatic compounds was studied and confirmed.
Keywords: Aliphatic alcohol sulfation; Amine sulfation; Arylsulfate sulfotransferase; Disulfated compounds; Enzymatic sulfation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
New Bacterial Aryl Sulfotransferases: Effective Tools for Sulfation of Polyphenols.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Oct 9;72(40):22208-22216. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c06771. Epub 2024 Oct 1. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 39351615 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Aryl Sulfotransferases in Selective and Sustainable Sulfation of Biologically Active Compounds using Novel Sulfate Donors.ChemSusChem. 2022 Sep 20;15(18):e202201253. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202201253. Epub 2022 Jul 28. ChemSusChem. 2022. PMID: 35832026
-
Kinetic mechanism and identification of the active site tyrosine residue in Enterobacter amnigenus arylsulfate sulfotransferase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Jul 13;285(2):526-9. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5185. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11444874
-
Sulfation and sulfotransferases 5: the importance of 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) in the regulation of sulfation.FASEB J. 1997 May;11(6):404-18. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.11.6.9194521. FASEB J. 1997. PMID: 9194521 Review.
-
Current status of the cytosolic sulfotransferases in the metabolic activation of promutagens and procarcinogens.Curr Drug Metab. 2000 Jul;1(1):1-30. doi: 10.2174/1389200003339234. Curr Drug Metab. 2000. PMID: 11467078 Review.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410. 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2 - PubMed
-
- Ayuso-Fernández I, Galmés MA, Bastida A, García-Junceda E (2014) Aryl sulfotransferase from Haliangiumochraceum: a versatile tool for the sulfation of small molecules. ChemCatChem 6(4):1059–1065. 10.1002/cctc.201300853
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

