LNK/SH2B3 Loss Exacerbates the Development of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms in CBL-deficient Mice
- PMID: 39560864
- PMCID: PMC11976319
- DOI: 10.1007/s12015-024-10825-0
LNK/SH2B3 Loss Exacerbates the Development of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms in CBL-deficient Mice
Abstract
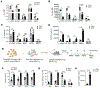
Genetic variations of signaling modulator protein LNK (also called SH2B3) are associated with relatively mild myeloproliferative phenotypes in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN). However, these variations can induce more severe MPN disease and even leukemic transformation when co-existing with other driver mutations. In addition to the most prevalent driver mutation JAK2V617F, LNK mutations have been clinically identified in patients harboring CBL inactivation mutations, but its significance remains unclear. Here, using a transgenic mouse model, we demonstrated that mice with the loss of both Lnk and Cbl exhibited severe splenomegaly, extramedullary hematopoiesis and exacerbated myeloproliferative characteristics. Moreover, a population of Mac1+ myeloid cells expressed c-Kit in aged mice. Mechanistically, we discovered that LNK could pull down multiple regulatory subunits of the proteosome. Further analysis confirmed a positive role of LNK in regulating proteasome activity, independent of its well-established function in signaling transduction. Thus, our work reveals a novel function of LNK in coordinating with the E3 ligase CBL to regulate myeloid malignancies.
Keywords: CBL; Leukemia; MPN; Proteasome; SH2B3.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical Approval: All the animal studies were performed under an approved protocol by the Institutional Animal Care and Use committee of Hunan University. Consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
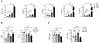
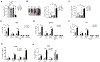
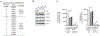

Similar articles
-
SH2B3 (LNK) mutations from myeloproliferative neoplasms patients have mild loss of function against wild type JAK2 and JAK2 V617F.Br J Haematol. 2013 Jun;161(6):811-20. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12327. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Br J Haematol. 2013. PMID: 23590807 Free PMC article.
-
CBL family E3 ubiquitin ligases control JAK2 ubiquitination and stability in hematopoietic stem cells and myeloid malignancies.Genes Dev. 2017 May 15;31(10):1007-1023. doi: 10.1101/gad.297135.117. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 28611190 Free PMC article.
-
The role of LNK/SH2B3 genetic alterations in myeloproliferative neoplasms and other hematological disorders.Leukemia. 2017 Aug;31(8):1661-1670. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.139. Epub 2017 May 9. Leukemia. 2017. PMID: 28484264 Review.
-
Expression level and differential JAK2-V617F-binding of the adaptor protein Lnk regulates JAK2-mediated signals in myeloproliferative neoplasms.Blood. 2010 Dec 23;116(26):5961-71. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-12-256768. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20870899
-
LNK mutations and myeloproliferative disorders.Am J Hematol. 2016 Feb;91(2):248-51. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24259. Am J Hematol. 2016. PMID: 26660394 Review.
References
-
- Watowich SS, et al. (1996). Cytokine receptor signal transduction and the control of hematopoietic cell development. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 12, 91–128. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

