Growth monitoring and promotion service utilization and its associated factors among children less than two years in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39561142
- PMCID: PMC11575828
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311531
Growth monitoring and promotion service utilization and its associated factors among children less than two years in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Growth monitoring and promotion services are strategies to promote child health and reduce child mortality. Even though Ethiopia is attempting different strategies to cope with the low rate of GMP utilization, the problem is still unresolved.
Objective: Determine the pooled proportion of GMP utilization and its contributing factors among children less than two years in Ethiopia.
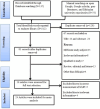
Method: The review protocol was registered with PROSPERO, number CRD42023472746. The PRISMA-2020 statement guided the conduct of this review. Electronic databases and grey literature were used. Heterogeneity was evaluated using I2. Subgroup analysis was conducted. The random effect model was used to summarize the pooled effect sizes with their respective 95% CI with STATA version 17. To test the small study effect, the funnel plot and Egger's test were applied.
Result: A total of seven (7) studies with 4027 participants were considered in this meta-analysis. The pooled proportion of GMP utilization reported by seven studies was 25.71% (95%CI: 24.39, 27.04). ANC follow-up (AOR = 2.11; 95% CI: 1.47, 2.76), PNC follow-up (AOR = 1.96; 95% CI: 1.44, 2.49), counseling (AOR = 2.88; 95% CI: 2.09, 3.68), maternal education (AOR = 2.89; 95% CI: 1.66, 4.13), paternal education (AOR = 3.78; 95% CI: 2.25, 5.32), family health card (AOR = 2.31; 95% CI: 1.67, 2.96), and mothers good knowledge towards GMP (AOR = 2.90; 95% CI: 1.72, 4.07) variables were positively associated with GMP service utilization.
Conclusion and recommendation: The pooled proportion of GMP remains low in Ethiopia. ANC and PNC follow-up, counseling, maternal and paternal education, family health cards, maternal knowledge towards GMP were significantly associated. Findings are essential for evidence-based policy making, intervention, and input for ongoing research.
Copyright: © 2024 Simegn et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Growth monitoring and promotion service utilization and its associated factors among mothers of children under two years in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Jul 19;24(1):463. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04946-1. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39030568 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Monitoring and Promotion Service Utilization and Associated Factors Among Mothers/Caregivers of Children 0-23 Months in Sude District, Southeast Ethiopia.Matern Child Nutr. 2025 Apr;21(2):e13769. doi: 10.1111/mcn.13769. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Matern Child Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39604193 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Diversity and Associated Factors among Children 6-23 Months Old in Ethiopia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Discov Med. 2024 Jul;36(186):1527-1543. doi: 10.24976/Discov.Med.202436186.141. Discov Med. 2024. PMID: 39054722
-
Utilization of growth monitoring and promotion services and associated factors among under two years of age children in Southern Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2017 May 16;12(5):e0177502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177502. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28510596 Free PMC article.
-
Institutional delivery service utilization and associated factors in Ethiopia: a systematic review and META-analysis.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020 Jun 15;20(1):364. doi: 10.1186/s12884-020-03032-5. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020. PMID: 32539698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jones A.D., et al.., World Health Organization infant and young child feeding indicators and their associations with child growth: a synthesis of recent findings. 2013, Wiley Online Library.
-
- Fanzo J., et al.., 2018 global nutrition report. 2019.
-
- Ethiopia F., Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey 2016. Addis Ababa Ethiopia, and Rockville. 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

