Do penguins care about their neighborhood? Population implications of bioerosion in Magellanic penguin, Spheniscus magellanicus, at Martillo Island, Beagle Channel, Argentina
- PMID: 39561201
- PMCID: PMC11575772
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310052
Do penguins care about their neighborhood? Population implications of bioerosion in Magellanic penguin, Spheniscus magellanicus, at Martillo Island, Beagle Channel, Argentina
Abstract
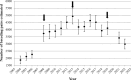
Intrinsic and extrinsic factors, such as bioerosion at nesting sites, regulate population dynamics and are relevant for the long-term conservation of penguins. Colony trends (between 2004-2022) were studied in a Magellanic penguin colony on Martillo Island, Beagle Channel, Argentina and compared between zones with contrasting degrees of erosion (high, medium, low). Individuals from each zone were characterized for foraging ecology, stress, and reproductive performance during the 2017-2018 breeding season to better understand the colony dynamics. Changes in nest abundance varied in magnitude between nesting zones with different characteristics of occupation time, density and erosion. Declines in nest abundance in the densest, most eroded and longest occupied zone suggests that environmental degradation may be limiting the colony's carrying capacity. A higher percentage of late breeders (probably younger breeders) occupied the less eroded and more recently occupied zone. Foraging, breeding and stress barely differed between zones. New individuals recruiting into the breeding colony select less-eroded zones, either to reduce competition for nests or to avoid other effects of erosion and high-density areas. If this is the mechanism behind the shift in numbers throughout the island, we expect the island to be progressively occupied to the west. If competition or other density dependent factors are at play, a time will come when the vacant east side will begin to be recolonized by younger individuals. However, if erosion or other long-term effects spread throughout the island, recolonization may not occur and the colony may ultimately be abandoned as individuals search for new breeding grounds. Erosion at the breeding site may be a key factor in regional population trends of this burrow nesting species, by following an extinction / colonization of new sites process.
Copyright: © 2024 Scioscia et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
NO authors have competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Piatt JF, Harding AM, Shultz M, Speckman SG, Van Pelt TI, Drew GS, et al. Seabirds as indicators of marine food supplies: Cairns revisited. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2007; 352: 221–234.
-
- Lewison R, Oro D, Godley BJ, Underhill L, Bearhop S, Wilson RP, et al. Research priorities for seabirds: improving conservation & management in the 21st century. Endang Species Res. 2012; 17(2): 93–121.
-
- Berryman AA. Limiting factors and population regulation. Oikos. 2004; 105(3): 667–670.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

