RAD52 and ERCC6L/PICH have a compensatory relationship for genome stability in mitosis
- PMID: 39561207
- PMCID: PMC11614213
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011479
RAD52 and ERCC6L/PICH have a compensatory relationship for genome stability in mitosis
Abstract
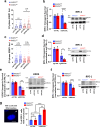
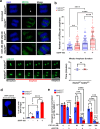
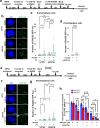
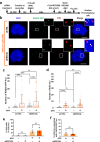
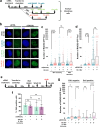
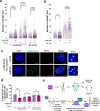
Mammalian RAD52 is a DNA repair factor with strand annealing and recombination mediator activities that appear important in both interphase and mitotic cells. Nonetheless, RAD52 is dispensable for cell viability. To query RAD52 synthetic lethal relationships, we performed genome-wide CRISPR knock-out screens and identified hundreds of candidate synthetic lethal interactions. We then performed secondary screening and identified genes for which depletion causes reduced viability and elevated genome instability (increased 53BP1 nuclear foci) in RAD52-deficient cells. One such factor was ERCC6L, which marks DNA bridges during anaphase, and hence is important for genome stability in mitosis. Thus, we investigated the functional interrelationship between RAD52 and ERCC6L. We found that RAD52 deficiency increases ERCC6L-coated anaphase ultrafine bridges, and that ERCC6L depletion causes elevated RAD52 foci in prometaphase and interphase cells. These effects were enhanced with replication stress (i.e. hydroxyurea) and topoisomerase IIα inhibition (ICRF-193), where post-treatment effect timings were consistent with defects in addressing stress in mitosis. Altogether, we suggest that RAD52 and ERCC6L co-compensate to protect genome stability in mitosis.
Copyright: © 2024 Osia et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Update of
-
RAD52 and ERCC6L/PICH have a compensatory relationship for genome stability in mitosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 23:2023.08.23.554522. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.23.554522. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Genet. 2024 Nov 19;20(11):e1011479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011479. PMID: 37662271 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
RAD52 and ERCC6L/PICH have a compensatory relationship for genome stability in mitosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 23:2023.08.23.554522. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.23.554522. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Genet. 2024 Nov 19;20(11):e1011479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011479. PMID: 37662271 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Bloom's syndrome and PICH helicases cooperate with topoisomerase IIα in centromere disjunction before anaphase.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033905. Epub 2012 Apr 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22563370 Free PMC article.
-
RAD52-dependent mitotic DNA synthesis is required for genome stability in Cyclin E1-overexpressing cells.Cell Rep. 2024 Apr 23;43(4):114116. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114116. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38625790
-
A moving target for drug discovery: Structure activity relationship and many genome (de)stabilizing functions of the RAD52 protein.DNA Repair (Amst). 2022 Dec;120:103421. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2022.103421. Epub 2022 Oct 27. DNA Repair (Amst). 2022. PMID: 36327799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corrupting the DNA damage response: a critical role for Rad52 in tumor cell survival.Aging (Albany NY). 2017 Jul 15;9(7):1647-1659. doi: 10.18632/aging.101263. Aging (Albany NY). 2017. PMID: 28722656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

