Quality of Life in Subcutaneous or Transvenous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Patients: A Secondary Analysis of the PRAETORIAN Trial
- PMID: 39561235
- PMCID: PMC11575910
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.124.010822
Quality of Life in Subcutaneous or Transvenous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Patients: A Secondary Analysis of the PRAETORIAN Trial
Abstract
Background: The subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (S-ICD) was developed to overcome the risk of lead-related complications associated with the transvenous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (TV-ICD). In contrast to the TV-ICD, the S-ICD is a completely extrathoracic device. Subsequently, complications differ between these 2 implantable cardioverter-defibrillators, which might impact patient perceptions of the therapies. This prespecified secondary analysis of the PRAETORIAN trial evaluates differences in quality of life.
Methods: The PRAETORIAN trial (A Prospective, Randomized Comparison of Subcutaneous and Transvenous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Therapy) randomized patients with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator indication, without the need for pacing to S-ICD or TV-ICD therapy. Two questionnaires were collected at baseline, discharge, 12 months, and 30 months. The Duke Activity Status Index measures cardiac-specific physical functioning, and the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey measures physical and mental well-being, with the subscales bodily pain and mental health being of interest in this analysis. Mann-Whitney U tests were used to compare study arms, and a mixed model was used to describe the questionnaire outcomes over time.
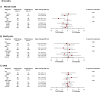
Results: Patients were randomized to S-ICD (n=426) and TV-ICD (n=423). In the S-ICD group, 20% were women versus 19% in the TV-ICD group. The median age was 63 (interquartile range, 54-69) years in the S-ICD group versus 64 (interquartile range, 56-69) years in the TV-ICD group. There were no significant differences in the Duke Activity Status Index and 36-Item Short Form Health Survey subscales for bodily pain and mental health between the groups at any time point. Patients with a shock in the last 90 days had significantly lower scores for social functioning (P=0.008) and role limitations due to emotional problems (P=0.001) than patients without a shock, but this effect did not differ between treatment arms.
Conclusions: In a large randomized cohort of patients with an S-ICD or TV-ICD, no difference in overall quality of life was observed. However, implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks resulted in a reduction in quality of life, regardless of the device type or appropriateness.
Registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; Unique identifier: NCT01296022.
Keywords: arrhythmias, cardiac; defibrillators, implantable; mental health; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Knops reports consultancy fees and research grants from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Cairdac and has stock options from AtaCor Medical, Inc. Dr El Chami reports consultancy fees from Boston Scientific and Medtronic. Dr Mittal reports consultancy fees from Boston Scientific and Medtronic. K.M. Kooiman reports consultancy fees from Boston Scientific. Dr Lambiase reports educational and research grants from and is in the research board of Boston Scientific, and reports research grants from Abbott. Dr Vernooy reports consultancy fees from Medtronic and Abbott. M.C. Burke is a consultant and receives honoraria, as well as research grants from Boston Scientific and has equity in and is chief medical officer for AtaCor Medical, Inc. Dr Wright has consultancy arrangements with Boston Scientific and Medtronic and iRhythm and a research grant from Boston Scientific. Dr Nordbeck reports modest speaker honoraria from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic. Dr Miller reports consultancy fees from Boston Scientific. Dr Whinnett is an advisor for Boston Scientific and is on the advisory board for Medtronic and Abbot and reports speaker fees from Medtronic. The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures



References
-
- Bardy GH, Lee KL, Mark DB, Poole JE, Packer DL, Boineau R, Domanski M, Troutman C, Anderson J, Johnson G, et al. ; Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure Trial (SCD-HeFT) Investigators. Amiodarone or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:225–237. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043399 - PubMed
-
- Moss AJ, Hall WJ, Cannom DS, Daubert JP, Higgins SL, Klein H, Levine JH, Saksena S, Waldo AL, Wilber D, et al. Improved survival with an implanted defibrillator in patients with coronary disease at high risk for ventricular arrhythmia. Multicenter automatic defibrillator implantation trial investigators. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1933–1940. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199612263352601 - PubMed
-
- Zeppenfeld K, Tfelt-Hansen J, de Riva M, Winkel BG, Behr ER, Blom NA, Charron P, Corrado D, Dagres N, de Chillou C, et al. 2022 ESC guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Eur Heart J. 2022;43:3997–4126. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac262 - PubMed
-
- Bardy GH, Smith WM, Hood MA, Crozier IG, Melton IC, Jordaens L, Theuns D, Park RE, Wright DJ, Connelly DT, et al. An entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:36–44. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0909545 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

