Changes in gut microbiota predict neutropenia after induction treatment in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 39561377
- PMCID: PMC11985026
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024013986
Changes in gut microbiota predict neutropenia after induction treatment in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
Delayed neutrophil recovery during acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) treatment increases the risk of infection and causes delay in chemotherapy. Emerging evidence implicates gut microbiota in neutrophil reconstitution after chemotherapy. We explored the interplay between the gut microbiota and neutrophil dynamics, including neutrophil chemoattractants, in 51 children with newly diagnosed ALL. Daily absolute neutrophil count (ANC), weekly plasma chemokines (CXCL1 and CXCL8), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), and fecal samples were monitored until day 29 during ALL induction treatment. Fecal sequencing using 16S ribosomal RNA revealed an overall significant reduction in bacterial diversity and Enterococcus overgrowth throughout the induction treatment. Prolonged neutropenia (ANC <0.5 × 109 cells per L at day 36) and elevated chemokine levels were associated with a decreased abundance of genera from the Ruminococcaceae and Lachnospiraceae families, decreased Veillonella genus, and Enterococcus overgrowth from diagnosis and throughout induction treatment. G-CSF was upregulated in response to neutropenia but was unrelated to microbiota changes. Overall, this study revealed that a diminished abundance of specific intestinal commensals and Enterococcus overgrowth is associated with delayed neutrophil reconstitution and increased chemokine signaling, indicating that disruption of the microbiota may contribute to prolonged neutropenia. These findings lay the groundwork for future investigations into the mechanisms underlying these associations and their clinical implications for developing gut-sparring strategies to minimize the impact of gut dysbiosis on immune recovery.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




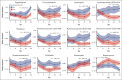

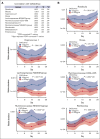
References
-
- Schmiegelow K, Forestier E, Hellebostad M, et al. Long-term results of NOPHO ALL-92 and ALL-2000 studies of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2010;24(2):345–354. - PubMed
-
- Afzal S, Ethier MC, Dupuis LL, et al. Risk factors for infection-related outcomes during induction therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009;28(12):1064–1068. - PubMed
-
- Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(3):159–175. - PubMed
-
- Balmer ML, Schürch CM, Saito Y, et al. Microbiota-derived compounds drive steady-state granulopoiesis via MyD88/TICAM signaling. J Immunol. 2014;193(10):5273–5283. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

