Truncating the C terminus of formate dehydrogenase leads to improved preference to nicotinamide cytosine dinucleotide
- PMID: 39562703
- PMCID: PMC11576888
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79885-z
Truncating the C terminus of formate dehydrogenase leads to improved preference to nicotinamide cytosine dinucleotide
Abstract
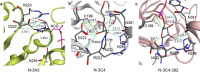
Formate dehydrogenase (FDH) is widely applied in regeneration of redox cofactors. There are continuing interests to engineer FDH for improved catalytic activity and cofactor preference. In the crystal structure of FDH from Pseudomonas sp. 101 (pseFDH), the C terminus with 9 amino acid residues cannot be resolved. However, our earlier work showed mutations at C terminus led pseFDH variants to favor a non-natural cofactor nicotinamide cytosine dinucleotide (NCD). Here, we investigated the role of C-terminal residues on cofactor preference by truncating their corresponding C terminus of pseFDH variants. Sequence comparison analysis showed that C-terminal residues were barely conservative among different FDHs. pseFDH and mutants with their C termini truncated were constructed, and the resulted variants showed improved preference to NCD mainly because NAD-dependent activity dropped more substantially. Further structure analysis showed that these pseFDH variants had their cofactor binding domains reconstructed to favor molecular interactions with NCD. Our work indicated that C-terminal residues of pseFDH affected enzyme activity and cofactor preference, which provides a new approach for ameliorating the performance of redox enzymes.
Keywords: C terminus; Cofactor preference; Directed evolution; Formate dehydrogenase; Non-natural cofactor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Shabalin, I. G. et al. Structures of the apo and holo forms of formate dehydrogenase from the bacterium Moraxella sp. C-1: towards understanding the mechanism of the closure of the interdomain cleft. Acta Cryst.D65, 1315–1325 (2009). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

