Impaired physical ability in patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia: Can regular physical activity be a countermeasure?
- PMID: 39562756
- PMCID: PMC11739766
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.19847
Impaired physical ability in patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia: Can regular physical activity be a countermeasure?
Abstract
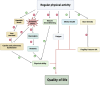
Transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia (TDβT) is a genetic disorder characterised by reduced or absent β-globin chain synthesis, resulting in chronic anaemia. Treatment consists of regular blood transfusions and chelation therapy to limit iron overload and its negative effects on organs (e.g. heart, lungs and liver). Despite improved life expectancy with transfusions and chelation therapy, TDβT patients experience poor quality of life and impaired exercise capacity (mainly due to muscle deconditioning and reduced cardiac inotropism). The aims of this review are (i) to discuss the role of organ dysfunction in the impairment of exercise capacity and reduced quality of life of TDβT patients; and (ii) to discuss physical activity as a potential therapeutic strategy to alleviate the multifactorial impact of the disease.
Keywords: muscle; physical exercise; thalassaemia; transfusion.
© 2024 The Author(s). British Journal of Haematology published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Cazzola M, Borgna‐Pignatti C, Locatelli F, Ponchio L, Beguin Y, De Stefano P. A moderate transfusion regimen may reduce iron loading in beta‐thalassemia major without producing excessive expansion of erythropoiesis. Transfusion. 1997;37(2):135–140. - PubMed
-
- Cracowski C, Wuyam B, Klein V, Lévy P. Lung function and exercise capacity in thalassaemia major. Eur Respir J. 1998;12(5):1130–1136. - PubMed
-
- Thompson AA, Walters MC, Kwiatkowski J, Rasko JEJ, Ribeil JA, Hongeng S, et al. Gene therapy in patients with transfusion‐dependent β‐thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(16):1479–1493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

