Increased adverse pregnancy outcomes among decreased assisted reproductions during the COVID-19 pandemic: insights from a birth cohort study in Southwest China
- PMID: 39563259
- PMCID: PMC11575422
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-024-06935-9
Increased adverse pregnancy outcomes among decreased assisted reproductions during the COVID-19 pandemic: insights from a birth cohort study in Southwest China
Abstract
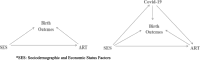
Objectives: We elucidate the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on assisted reproductive technology (ART) services and birth outcomes and establish an evidence-based framework to maintain the high quality of ART healthcare services and ensure continuous improvement of birth outcomes.
Methods: A total of 19,170 pregnant women from Sichuan, Guizhou and Chongqing in Southwest China between 2018 and 2021 were included in this study. The log-binomial regression model was employed to analyse the changes in the probability of adverse birth outcomes, such as low birth weight (LBW), preterm birth (PTB), Apgar score < 7 at 1 min and congenital anomalies (CAs) and their relationship with ART before and after the pandemic. In this analysis, confounding factors such as family annual income, maternal ethnicity, delivery age, subjective prenatal health status, vitamin or mineral supplementation during pregnancy and level of prenatal care provided by the hospital were controlled.
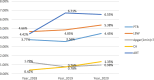
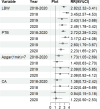
Results: ART mothers had the highest probability of giving birth to LBW babies (relative risk (RR): 2.82, 95% confidence interval (CI): 2.32-3.41), experiencing PTB (RR: 2.72, 95% CI: 2.78-3.22) and delivering babies with an Apgar score < 7 at 1 min (RR: 1.73, 95% CI: 1.05-2.69). Before the pandemic, the ART rate increased from 4.42% in 2018 to 6.71% in 2019 (rate difference of 2.29%, P < 0.001). After the pandemic, the ART rate decreased from 6.71% in 2019 to 6.55% in 2020 (rate difference of - 0.16%, P = 0.752). Compared with the pre-pandemic period, the rate difference for LBW decreased from - 0.21% (P = 0.646) in 2018-2019 to an increase of + 0.89% (P = 0.030) in 2019-2020. Similarly, PTB showed an increase in rate difference from + 0.20% (P = 0.623) before the pandemic to + 0.53% (P = 0.256) afterwards. Apgar score < 7 at 1 min had a negative rate difference of - 0.50% (P = 0.012), which changed to a positive value of + 0.20% (P = 0.340). For CAs, the rate difference increased from + 0.34% (P = 0.089) prior to the outbreak to + 0.59% (P = 0.102) at post-outbreak. In 2018 (pre-pandemic), ART was the most significant predictor of LBW, exhibiting an RR of 3.45 (95% CI: 2.57-4.53). Furthermore, in 2020, its RR was 2.49 (95% CI: 1.78-3.42). Prior to the onset of the pandemic (2018), ART (RR: 3.17, 95% CI: 2.42-4.08) was the most robust predictor of PTB. In 2020, its RR was 2.23 (95% CI: 1.65-2.97).
Conclusion: ART services have been significantly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, and the resulting delays in ART services have had notable implications for maternal birth outcomes.
Keywords: Apgar; CA; COVID-19; LBW; PTB.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Zheng Y, Dong J. Comparison and analysis of clinical data characteristics of assisted reproduction between different countries and regions. J Reprod Med. 2024;33(2):187–93.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

