NIRSpredict: a platform for predicting plant traits from near infra-red spectroscopy
- PMID: 39563275
- PMCID: PMC11577922
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-024-05776-0
NIRSpredict: a platform for predicting plant traits from near infra-red spectroscopy
Abstract
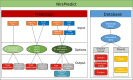
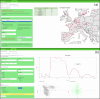
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) has become a popular tool for investigating phenotypic variability in plants. We developed the Shiny NIRSpredict application to get predictions of 81 Arabidopsis thaliana phenotypic traits, including classical functional traits as well as a large variety of commonly measured chemical compounds, based from near-infrared spectroscopy values based on deep learning. It is freely accessible at the following URL: https://shiny.cefe.cnrs.fr/NirsPredict/ . NIRSpredict has three main functionalities. First, it allows users to submit their spectrum values to get the predictions of plant traits from models built with the hosted A. thaliana database. Second, users have access to the database of traits used for model calibration. Data can be filtered and extracted on user's choice and visualized in a global context. Third, a user can submit his own dataset to extend the database and get part of the application development. NIRSpredict provides an easy-to-use and efficient method for trait prediction and an access to a large dataset of A. thaliana trait values. In addition to covering many of functional traits it also allows to predict a large variety of commonly measured chemical compounds. As a reliable way of characterizing plant populations across geographical ranges, NIRSpredict can facilitate the adoption of phenomics in functional and evolutionary ecology.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; Functional traits; Genetic variability; Machine learning; Phenomics; Secondary metabolites; Trait prediction.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Violle C, Navas M-L, Vile D, Kazakou E, Fortunel C, Hummel I, et al. Let Concept Trait be Functional! Oikos. 2007;116:882–92. 10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15559.x.
-
- Garnier E, Navas M-L, Grigulis K. Plant Functional Diversity Organism traits, community structure, and ecosystem properties. 2016. 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198757368.001.0001
-
- Foley WJ, Aragones L. Ecological applications of near infrared re¯ectance spectroscopy ± a tool for rapid, cost-effective prediction of the composition of plant and animal tissues and aspects of animal performance n.d.:13. - PubMed
-
- Pasquini C. Near infrared spectroscopy: a mature analytical technique with new perspectives – A review. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1026:8–36. 10.1016/j.aca.2018.04.004. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

