Gut metatranscriptomics based de novo assembly reveals microbial signatures predicting immunotherapy outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39563352
- PMCID: PMC11577905
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05835-y
Gut metatranscriptomics based de novo assembly reveals microbial signatures predicting immunotherapy outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) poses treatment challenges, with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) as the main therapy. Emerging evidence suggests the gut microbiome significantly influences ICI efficacy. This study explores the link between the gut microbiome and ICI outcomes in NSCLC patients, using metatranscriptomic (MTR) signatures.
Methods: We utilized a de novo assembly-based MTR analysis on fecal samples from 29 NSCLC patients undergoing ICI therapy, segmented according to progression-free survival (PFS) into long (> 6 months) and short (≤ 6 months) PFS groups. Through RNA sequencing, we employed the Trinity pipeline for assembly, MMSeqs2 for taxonomic classification, DESeq2 for differential expression (DE) analysis. We constructed Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) machine learning (ML) algorithms and comprehensive microbial profiles.
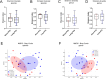
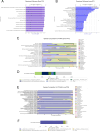
Results: We detected no significant differences concerning alpha-diversity, but we revealed a biologically relevant separation between the two patient groups in beta-diversity. Actinomycetota was significantly overrepresented in patients with short PFS (vs long PFS, 36.7% vs. 5.4%, p < 0.001), as was Euryarchaeota (1.3% vs. 0.002%, p = 0.009), while Bacillota showed higher prevalence in the long PFS group (66.2% vs. 42.3%, p = 0.007), when comparing the abundance of corresponding RNA reads. Among the 120 significant DEGs identified, cluster analysis clearly separated a large set of genes more active in patients with short PFS and a smaller set of genes more active in long PFS patients. Protein Domain Families (PFAMs) were analyzed to identify pathways enriched in patient groups. Pathways related to DNA synthesis and Translesion were more enriched in short PFS patients, while metabolism-related pathways were more enriched in long PFS patients. E. coli-derived PFAMs dominated in patients with long PFS. RF, SVM and XGBoost ML models all confirmed the predictive power of our selected RNA-based microbial signature, with ROC AUCs all greater than 0.84. Multivariate Cox regression tested with clinical confounders PD-L1 expression and chemotherapy history underscored the influence of n = 6 key RNA biomarkers on PFS.
Conclusion: According to ML models specific gut microbiome MTR signatures' associate with ICI treated NSCLC outcomes. Specific gene clusters and taxa MTR gene expression might differentiate long vs short PFS.
Keywords: De novo assembly; Gut microbiome; Immune-checkpoint inhibitor; Immunotherapy; Machine learning; Metatranscriptome; Progression-free survival.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, Domine M, Clingan P, Hochmair MJ, Powell SF, Cheng SY, Bischoff HG, Peled N, Grossi F, Jennens RR, Reck M, Hui R, Garon EB, Boyer M, Rubio-Viqueira B, Novello S, Kurata T, Gray JE, Vida J, Wei Z, Yang J, Raftopoulos H, Pietanza MC, Garassino MC, KEYNOTE-189 Investigators. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(22):2078–92. 10.1056/NEJMoa1801005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dora D, Ligeti B, Kovacs T, Revisnyei P, Galffy G, Dulka E, Krizsán D, Kalcsevszki R, Megyesfalvi Z, Dome B, Weiss GJ, Lohinai Z. Non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with Anti-PD1 immunotherapy show distinct microbial signatures and metabolic pathways according to progression-free survival and PD-L1 status. Oncoimmunology. 2023;12(1):2204746. 10.1080/2162402X.2023.2204746. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Routy B, Le Chatelier E, Derosa L, Duong CPM, Alou MT, Daillère R, Fluckiger A, Messaoudene M, Rauber C, Roberti MP, Fidelle M, Flament C, Poirier-Colame V, Opolon P, Klein C, Iribarren K, Mondragón L, Jacquelot N, Qu B, Ferrere G, Clémenson C, Mezquita L, Masip JR, Naltet C, Brosseau S, Kaderbhai C, Richard C, Rizvi H, Levenez F, Galleron N, Quinquis B, Pons N, Ryffel B, Minard-Colin V, Gonin P, Soria JC, Deutsch E, Loriot Y, Ghiringhelli F, Zalcman G, Goldwasser F, Escudier B, Hellmann MD, Eggermont A, Raoult D, Albiges L, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L. Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science. 2018;359(6371):91–7. 10.1126/science.aan3706. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- #146775/National Research, Development and Innovation Office
- #142287/National Research, Development and Innovation Office
- UNKP-23-5/New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology of Hungary
- Bolyai Research Scholarship/Magyar Tudományos Akadémia
- #138055/Nemzeti Kutatási, Fejlesztési és Innovaciós Alap
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

