Role of social innovations in health in the prevention and control of infectious diseases: a scoping review
- PMID: 39563417
- PMCID: PMC11577845
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-024-01253-w
Role of social innovations in health in the prevention and control of infectious diseases: a scoping review
Abstract
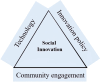
Background: The implementation of social innovations for addressing societal challenges, particularly in health, leverages community participation and technology to optimally meet social needs compared to traditional approaches. A key feature of these innovations is their ability to utilize existing capacities for contributing to resolving infectious disease outbreaks, which has attracted significant attention from health organizations. Given the potential of these innovations, this study has investigated social innovations in the prevention and control of infectious diseases as one of the major global challenges in the form of a comprehensive literature review.
Methods: This review study examined the relevant literature from January 1, 2010 to December 31, 2022. Based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, 50 documents were retained and fully examined. The documents were analyzed by applying a thematic analysis, and important content related to the application of social innovations for the prevention and control of pandemic infectious diseases was extracted using a data collection form.
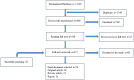
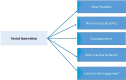
Results: Five major themes concerning social innovation in the prevention and control of epidemic diseases were discerned as follows: new products, novel processes and policies, empowerment, innovative practices and behaviors, and community engagement. New products include technological products for control and management of epidemics, preventive products, diagnostic and therapeutic products. Novel processes and policies are related to reorienting and reorganizing care methods, control and monitoring policies, participatory and creative strategies. Empowerment is focused on enhancing the capabilities of health workers, community leaders, and communities. Innovative practices and behaviors involve technology-based participation and support mechanisms. Community engagement is related to awareness, consultation, community mobilization, and participation in production and support.
Conclusions: During the outbreak of infectious diseases, governments are faced with many challenges, including health, economic and social challenges. To answer these challenges, tools should be used that have the ability to answer the problem from several aspects. Social innovation as an appropriate process in response to health crises has led to new forms of relationships and empowered the communities. And to promote public health, it provides the opportunity for all members of the society to participate in crisis resolution and optimal use of resources.
Keywords: COVID-19; Control; Infectious disease; Prevention; Social innovation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Moura M, Perez IU, Melara LF, Junior JCM. Contemporary design in quarantine: a critical review of design responses to COVID-19 crisis. SDRJ. 2020;13(3):327–41. 10.4013/sdrj.2020.133.03.
-
- Mukherjee K. Integrating technology, innovation and policy: COVID-19 and HTA. Health Policy Technol. 2021;10(1):16–20. 10.1016/j.hlpt.2021.01.003.
-
- Kranzeeva E, Golovatsky E, Orlova A, Nyatina N, Burmakina A. Assessing the effectiveness of social and political innovations in the development of interaction between the authorities and the population during COVID-19: the implication of open innovation. JOItmC. 2021;7(3):172. 10.3390/joitmc7030172.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

