Localization of brain neuronal IL-1R1 reveals specific neural circuitries responsive to immune signaling
- PMID: 39563437
- PMCID: PMC11575132
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-024-03287-1
Localization of brain neuronal IL-1R1 reveals specific neural circuitries responsive to immune signaling
Abstract
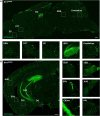
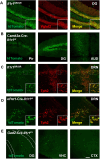
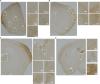
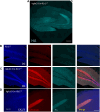
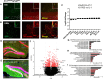
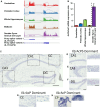
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that exerts a wide range of neurological and immunological effects throughout the central nervous system (CNS) and is associated with the etiology of affective and cognitive disorders. The cognate receptor for IL-1, Interleukin-1 Receptor Type 1 (IL-1R1), is primarily expressed on non-neuronal cells (e.g., endothelial cells, choroidal cells, ventricular ependymal cells, astrocytes, etc.) throughout the brain. However, the presence and distribution of neuronal IL-1R1 (nIL-1R1) has been controversial. Here, for the first time, a novel genetic mouse line that allows for the visualization of IL-1R1 mRNA and protein expression (Il1r1GR/GR) was used to map all brain nuclei and determine the neurotransmitter systems which express nIL-1R1 in adult male mice. The direct responsiveness of nIL-1R1-expressing neurons to both inflammatory and physiological levels of IL-1β in vivo was tested. Neuronal IL-1R1 expression across the brain was found in discrete glutamatergic and serotonergic neuronal populations in the somatosensory cortex, piriform cortex, dentate gyrus, and dorsal raphe nucleus. Glutamatergic nIL-1R1 comprises most of the nIL-1R1 expression and, using Vglut2-Cre-Il1r1r/r mice, which restrict IL-1R1 expression to only glutamatergic neurons, an atlas of glutamatergic nIL-1R1 expression across the brain was generated. Analysis of functional outputs of these nIL-1R1-expressing nuclei, in both Il1r1GR/GR and Vglut2-Cre-Il1r1r/r mice, reveals IL-1R1+ nuclei primarily relate to sensory detection, processing, and relay pathways, mood regulation, and spatial/cognitive processing centers. Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injections of IL-1 (20 ng) induces NFκB signaling in IL-1R1+ non-neuronal cells but not in IL-1R1+ neurons, and in Vglut2-Cre-Il1r1r/r mice IL-1 did not change gene expression in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus (DG). GO pathway analysis of spatial RNA sequencing 1mo following restoration of nIL-1R1 in the DG neurons reveals IL-1R1 expression downregulates genes related to both synaptic function and mRNA binding while increasing select complement markers (C1ra, C1qb). Further, DG neurons exclusively express an alternatively spliced IL-1R Accessory protein isoform (IL-1RAcPb), a known synaptic adhesion molecule. Altogether, this study reveals a unique network of neurons that can respond directly to IL-1 via nIL-1R1 through non-autonomous transcriptional pathways; earmarking these circuits as potential neural substrates for immune signaling-triggered sensory, affective, and cognitive disorders.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Avital A, Goshen I, Kamsler A, Segal M, Iverfeldt K, Richter-Levin G, Yirmiya R. Impaired interleukin-1 signaling is associated with deficits in hippocampal memory processes and neural plasticity. Hippocampus. 2003;13(7):826–34. 10.1002/hipo.10135. - PubMed
-
- Baganz NL, Lindler KM, Zhu CB, Smith JT, Robson MJ, Iwamoto H, Deneris ES, Hewlett WA, Blakely RD. A requirement of serotonergic p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase for peripheral immune system activation of CNS serotonin uptake and serotonin-linked behaviors. Translational Psychiatry. 2015;5(11):e671. 10.1038/tp.2015.168. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ban E, Milon G, Prudhomme N, Fillion G, Haour F. Receptors for interleukin-1 (α and β) in mouse brain: mapping and neuronal localization in hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1991;43(1):21–30. 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90412-h. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

