Resolving interfacial charge transfer in titanate superlattices using resonant x-ray reflectometry
- PMID: 39563732
- PMCID: PMC11574859
- DOI: 10.1103/physrevmaterials.2.093801
Resolving interfacial charge transfer in titanate superlattices using resonant x-ray reflectometry
Abstract
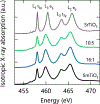
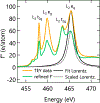
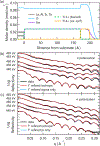
Charge transfer in oxide heterostructures can be tuned to promote emergent interfacial states, and accordingly, has been the subject of intense study in recent years. However, accessing the physics at these interfaces, which are often buried deep below the sample surface, remains difficult. Addressing this challenge requires techniques capable of measuring the local electronic structure with high-resolution depth dependence. Here, we used linearly polarized resonant x-ray reflectometry (RXR) as a means to visualize charge transfer in oxide superlattices with single unit cell precision. From our RXR measurements, we extract valence depth profiles of SmTiO3 (SmTO)/SrTiO3 (STO) heterostructures with STO quantum wells varying in thickness from five SrO planes down to a single SrO plane. At the polar-nonpolar SmTO/STO interface, an electrostatic discontinuity leads to approximately half an electron per areal unit cell transferred from the interfacial SmO layer into the neighboring STO quantum well. We observe this charge transfer as a suppression of the t 2g absorption peaks that minimizes contrast with the neighboring SmTO layers at those energies and leads to a pronounced absence of superlattice peaks in the reflectivity data. Our results demonstrate the sensitivity of RXR to electronic reconstruction in single unit cell layers, and establish RXR as a powerful means of characterizing charge transfer at buried oxide interfaces.
Figures


References
-
- Mimura T, Hiyamizu S, Fujii T, and Nanbu K, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 19, L225 (1980).
-
- Tsui DC, Stormer HL, and Gossard AC, Phys. Rev. Lett 48, 1559 (1982).
-
- Chambers SA, Adv. Mater 22, 219 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Boschker H and Mannhart J, Annu. Rev. Conden. Matter Phys 8, 145 (2017).
-
- Mannhart J and Schlom D, Science 327, 1607 (2010). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
