Whole Lung Lavage in Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: Unique Challenges in a Resource-Limited Setting
- PMID: 39563859
- PMCID: PMC11573727
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.9588
Whole Lung Lavage in Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: Unique Challenges in a Resource-Limited Setting
Abstract
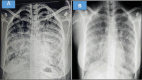
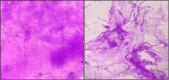
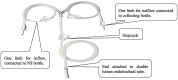
Autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is characterized by antibodies to granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), alveolar macrophage dysfunction, and surfactant accumulation. Whole lung lavage (WLL) is the treatment of choice in patients with PAP and severe hypoxemia. In resource-limited settings, WLL can be performed in the intubated, anesthetized patient who is being one lung ventilated using a Y-type bladder irrigation catheter for saline instillation and drainage.
Keywords: autoimmune PAP; bronchoalveolar lavage; pulmonary alveolar proteinosis; whole lung lavage.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ben‐Dov I., Kishinevski Y., Roznman J., et al., “Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis in Israel: Ethnic Clustering,” Israel Medical Association Journal 1 (1999): 75–78. - PubMed
-
- Holbert J. M., Costello P., Li W., Hoffman R. M., and Rogers R. M., “CT Features of Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis,” American Journal of Roentgenology 176, no. 5 (2001): 1287–1294. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

