Fabrication of crosslinker free hydrogels with diverse properties: An interplay of multiscale physical forces within polymer matrix
- PMID: 39563896
- PMCID: PMC11574810
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111227
Fabrication of crosslinker free hydrogels with diverse properties: An interplay of multiscale physical forces within polymer matrix
Abstract
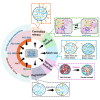
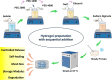
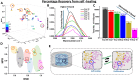
Physical/chemical crosslinking and surface-modifications of hydrogels have been extensively endorsed to enhance their biomaterial functionalities. The latter approaches involve using toxic crosslinkers or chemical modifications of the biopolymers, limiting the clinical translation of hydrogels beyond short-term promising results. The current study aims to tailor the polymer's structure to obtain customized applications using the same FDA-approved ingredients. PEGs of different molecular weights have been used to tune the van der Waal's forces, NaCl has been used to alter the electrostatic interactions of the charged polymers, and glycerol has been used to tweak the H-bonding. Same crosslinker-free sodium alginate/gelatin hydrogel formulation unfolds multiple properties: controlled-release, self-healing, mesh size, storage modulus, degradation rate. The hydrogels, lacking in one aspect, displayed superior performance in another. This study, including experiments and molecular simulations, illustrates that developing new materials may not always be necessary, as the same polymeric matrix can generate immense variations in different aspects.
Keywords: Materials science; Polymers.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

