Exploring the therapeutic mechanisms of heart failure with Chinese herbal medicine: a focus on miRNA-mediated regulation
- PMID: 39564110
- PMCID: PMC11573571
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1475975
Exploring the therapeutic mechanisms of heart failure with Chinese herbal medicine: a focus on miRNA-mediated regulation
Abstract
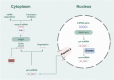
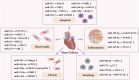
Heart failure (HF) is a clinical condition caused by abnormalities in the heart's structure or function, primarily manifested as diminished ability of the heart to pump blood, which leads to compensatory activation of neurohormones and increased left ventricular filling pressure. HF is one of the fastest-growing cardiovascular diseases globally in terms of incidence and mortality, negatively impacting patients' quality of life and imposing significant medical and economic burdens. Despite advancements in the treatment of HF, hospitalization and mortality remain rates high. In China, Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) has historically played a prominent role in addressing HF, with significant proven efficacy. MicroRNA (miRNA) exerts a pivotal regulatory influence on the maintenance of regular cardiac activity and the progression of HF. MiRNAs, a category of single-stranded RNA molecules, are characterized by their inability to code for proteins. They regulate gene expression by binding to the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of target mRNAs, thereby influencing the onset and progression of various diseases. Abnormal expression of specific miRNAs is closely associated with HF pathological processes, such as cardiomyocyte apoptosis, myocardial fibrosis, and cardiac hypertrophy. This abnormal expression can influence the pathological progression of HF through the regulation of miRNA expression. This article reviews the regulatory role of miRNAs in HF pathology discusses how CHM compounds and their active ingredients can ameliorate HF pathology through the regulation of miRNA expression. In conclusion, miRNAs represent promising therapeutic targets for HF, and CHM provides a novel strategy for treatment through the regulation of miRNA expression. Future studies must delve deeper into the precise mechanisms by which CHM modulates miRNAs and fully explore its potential for clinical application in HF treatment.
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine; apoptosis; cardiac fibrosis; cardiac hypertrophy; heart failure; microRNA; therapeutic strategies.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Lai, Chen, Sun, Ma and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer DL declared a shared affiliation with the author ZC to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and pharmacological mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicine for coronary heart disease complicated with heart failure.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 25;322:117605. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117605. Epub 2023 Dec 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38128892 Review.
-
The immune regulatory role of exosomal miRNAs and their clinical application potential in heart failure.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 2;15:1476865. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1476865. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39687609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNA changes in heart failure patients treated with cardiac resynchronization therapy: responders vs. non-responders.Eur J Heart Fail. 2013 Nov;15(11):1277-88. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hft088. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Eur J Heart Fail. 2013. PMID: 23736534 Clinical Trial.
-
MicroRNAs in the development of left ventricular remodeling and postmyocardial infarction heart failure.Pol Arch Intern Med. 2020 Jan 31;130(1):59-65. doi: 10.20452/pamw.15137. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 31933487 Review.
-
Regulation of cardiac microRNAs induced by aerobic exercise training during heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Nov 15;309(10):H1629-41. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00941.2014. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26408546
Cited by
-
A fibrin gel-loaded Gouqi-derived nanovesicle (GqDNV) repairs the heart after myocardial infarction by inhibiting p38 MAPK/NF-κB p65 pathway.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jul 22;23(1):535. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03615-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40696398 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous