Drug resistance and virulence-associated genes screening in Salmonella enterica isolated from Caspian pony, Iran
- PMID: 39564468
- PMCID: PMC11571046
- DOI: 10.30466/vrf.2024.2014684.4051
Drug resistance and virulence-associated genes screening in Salmonella enterica isolated from Caspian pony, Iran
Abstract
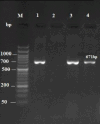
The most serious problem in public health is salmonellosis, a common disease in horse. The aim of this study was to investigate the shedding of Salmonella serotypes in healthy Caspian pony. We examined 143 pony's fecal samples collected from the north of Iran belonging to different ages and sexes. Samples were cultured, then identification of isolates were performed by common bacteriological methods and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The PCR was also used to explore the presence of fimA and salmonella secreted effector L (SseL) genes as virulence factors in the isolates and all were assigned to antibiotic susceptibility test via disc diffusion method. Results showed two fecal samples (1.39%) contaminated with Salmonella and further examination demonstrated the isolates belonging to S. enterica serotype typhimurium. Both serotypes were isolated from female and ˂6 years of age group of ponies and we detected fimA and SseL genes in the isolates. Observing multiple drug resistance and virulence genes in isolates is of utmost importance from both clinical and public health perspectives. It is highly likely that we face instances of salmonellosis in animals or humans that lead to severe infections and fail to respond to treatment in future. This study revealed that the occurrence of Salmonella was low in ponies, however, regarding the presence of virulence factors with multidrug resistant trend in this zoonotic bacterium, establishment of good hygienic measurement to prevent the transmission of bacteria between animal and human is necessary.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; Caspian pony; Salmonella; Virulence gene.
© 2024 Urmia University. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Colistin-, cefepime-, and levofloxacin-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from Egyptian chicken carcasses.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2024 Jul 4;23(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12941-024-00713-3. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2024. PMID: 38965586 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis isolated from poultry meat: virulence and antimicrobial-resistant genes.BMC Microbiol. 2023 Jun 15;23(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02908-8. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37322421 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, virulence factor and antimicrobial resistance analysis of Salmonella Enteritidis from poultry and egg samples in Iran.BMC Vet Res. 2021 May 24;17(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02900-2. BMC Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34030671 Free PMC article.
-
Serotype Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance among Salmonella enterica Isolates from Patients at an Equine Referral Hospital.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jun 18;84(13):e02829-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02829-17. Print 2018 Jul 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29678910 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of Salmonella serotypes among children in Iran: antimicrobial susceptibility, biofilm formation, and virulence genes.BMC Pediatr. 2022 Sep 21;22(1):557. doi: 10.1186/s12887-022-03614-6. BMC Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36131275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zahraei Salehi T, Gharagozlou MJ, Shams N, et al. Molecular characterization a Salmonella Typhimurium isolate from Caspian pony. Iran J Biotech. 2012;10(1):49–54.
-
- Cummings KJ, Perkins GA, Khatibzadeh SM, et al. Anti-microbial resistance trends among Salmonella isolates obtained from horses in the northeastern United States (2001-2013) Am J Vet Res. 2016;77(5):505–513. - PubMed
-
- Fakour S, Musavi Rad SA, Ahmadi E. A study on latent equine Salmonellosis based on phenotypic and molecular methods in Kurdistan province of Iran. Iran J Vet Med. 2020;14(4):352–360.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
