Effects of integrated blood purification on haemodynamics and oxygen metabolism in children with severe sepsis
- PMID: 39564495
- PMCID: PMC11573546
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1400154
Effects of integrated blood purification on haemodynamics and oxygen metabolism in children with severe sepsis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of integrated blood purification on haemodynamics and oxygen metabolism in children with severe sepsis.
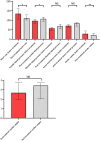
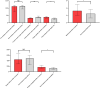
Methods: Clinical data of 12 children with severe sepsis admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit of our hospital between October 2021 and June 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. All patients were treated with integrated blood purification, and changes in haemodynamic parameters, including heart rate, blood pressure, mean arterial pressure and cardiac output, and oxygen metabolism parameters (blood lactic acid, oxygen delivery, oxygen consumption and oxygen extraction rate) were observed before and after treatment.
Results: The heart rate (134[106,160] vs 111[101,128], p = 0.037), central venous pressure (9[7,10] vs 8[7,9], p = 0.04), stroke output (28[18,43] vs 21[15,31], p = 0.01), blood lactate (3.3[2,4] vs 2.5[1.3,3.6], p = 0.015), oxygen consumption (165.99[121.44,230.31] vs 124.18[82.51,162.86], p = 0.041) and oxygen extraction rate (38.83[31.87,44.62] vs 28.67[21.05,32.72], p = 0.019) were decreased, whereas systolic blood pressure (97[83,104] vs 107[94,116], p = 0.033) and central venous oxygen pressure (32[29, 37] vs 39[34,46], p = 0.005) were increased in the children after treatment compared with before treatment. There were no statistically significant differences in diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, cardiac output, arterial oxygen pressure and oxygen delivery before and after treatment (all p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Integrated blood purification can improve haemodynamic and oxygen metabolism parameters in children with severe sepsis, with a high value in clinical application.
Keywords: blood purification; children; haemodynamics; oxygen metabolism; severe sepsis.
Copyright © 2024 Ma, Wang, Geng, Zhao, Wang, Liu, Xu, Liu, Wang, Zhao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of Xuebijing injection on hemodynamics and endothelial function in patients with severe sepsis: a prospective study].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Feb;27(2):127-32. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.02.010. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 25665612 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Effects of interposed abdominal pulling-pressing cardiopulmonary resuscitation on hemodynamics and oxygen metabolism in patients with cardiac arrest].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Nov;31(11):1406-1410. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.11.018. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31898574 Chinese.
-
[The value of maximal rate of left ventricular pressure in evaluating cardiac function in patients with sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Jun;35(6):620-626. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220412-00362. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37366129 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Haemodynamic monitoring. Problems, pitfalls and practical solutions.Drugs. 1991 Jun;41(6):857-74. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199141060-00004. Drugs. 1991. PMID: 1715263 Review.
-
The role of central venous oxygen saturation, blood lactate, and central venous-to-arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure difference as a goal and prognosis of sepsis treatment.J Crit Care. 2016 Dec;36:223-229. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.08.002. Epub 2016 Aug 10. J Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 27566006 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources