Effectiveness of Tai Chi exercise on balance, falls, and motor function in older adults: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 39564508
- PMCID: PMC11573509
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1486746
Effectiveness of Tai Chi exercise on balance, falls, and motor function in older adults: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study systematically evaluated Tai Chi's effects on balance, fall prevention, and physical function in older adults.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Web of Science, and EMbase databases included randomized controlled trials published up to August 2024. The meta-analysis used RevMan 5.4 and applied the GRADE framework to assess evidence quality.
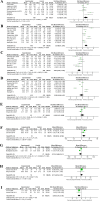
Results: Twenty-two studies met the criteria. Tai Chi significantly improved balance and physical function, particularly in the Berg Balance Scale (BBS), one-leg standing with eyes closed (OLS-C), and Timed up-and-go test (TUG). Fear of falling (FOF) also reduced, though changes in Tinetti Balance Test (TBT) and Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) were not statistically significant.
Conclusion: Tai Chi effectively enhances balance and physical function in older adults, with notable potential for fall risk reduction. While some tests showed no significant effect, overall results support Tai Chi as a valuable intervention to promote older adults' health.
Systematic review registration: https://inplasy.com/inplasy-2024-8-0082/.
Keywords: Tai Chi; balance; falls; older adults; physical functional abilities.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Guo, Ding and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tai Chi for fall prevention and balance improvement in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Public Health. 2023 Sep 1;11:1236050. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1236050. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37736087 Free PMC article.
-
Tai chi improves balance performance in healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Public Health. 2024 Nov 11;12:1443168. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1443168. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39588165 Free PMC article.
-
Balance and Functional Outcomes for Older Community-Dwelling Adults Who Practice Tai Chi and Those Who Do Not: A Comparative Study.J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2019 Oct/Dec;42(4):209-215. doi: 10.1519/JPT.0000000000000153. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2019. PMID: 29135600
-
Effectiveness of Tai Chi exercise on fear of falling and balance in older adults: A meta-analysis.Geriatr Nurs. 2023 May-Jun;51:194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2023.03.019. Epub 2023 Apr 1. Geriatr Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37011491
-
Tai Chi Chuan can improve balance and reduce fear of falling in community dwelling older adults: a randomized control trial.J Exerc Rehabil. 2018 Dec 27;14(6):1024-1031. doi: 10.12965/jer.1836488.244. eCollection 2018 Dec. J Exerc Rehabil. 2018. PMID: 30656165 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Effectiveness and Safety of Tai Chi on Knee Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jul 6;13(13):1615. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13131615. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global research on Chinese martial arts (1974-2025): A bibliometric and visualization-based analysis using Web of Science.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 8;104(32):e43769. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043769. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40797508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y, Zhang Y, Guo Z, Bao D, Zhou J. Comparison between the effects of exergame intervention and traditional physical training on improving balance and fall prevention in healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neuroeng Rehabil. (2021) 18:164. doi: 10.1186/s12984-021-00917-0, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferreira S, Marmeleira J, Del Pozo-Cruz J, Bernardino A, Leite N, Brandão M, et al. . Acute effects of augmented reality Exergames versus cycle ergometer on reaction time, visual attention, and verbal fluency in community older adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:14667. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214667, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pluchino A, Lee SY, Asfour S, Roos BA, Signorile JF. Pilot study comparing changes in postural control after training using a video game balance board program and 2 standard activity-based balance intervention programs. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2012) 93:1138–46. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2012.01.023, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

