Differential modulation of pain and associated anxiety by GABAergic neuronal circuits in the lateral habenula
- PMID: 39565313
- PMCID: PMC11621741
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2409443121
Differential modulation of pain and associated anxiety by GABAergic neuronal circuits in the lateral habenula
Abstract
Persistent pain frequently precipitates the development of anxiety disorders, yet the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. In this study, we employed a mouse model that simulates trigeminal neuralgia and observed a marked reduction in the activity of GABAergic neurons in the lateral habenula (LHb), a critical region for modulating pain and anxiety. We utilized precise optogenetic and chemogenetic techniques to modulate these neurons, which significantly alleviated behaviors associated with pain and anxiety. Our investigations revealed an inhibitory pathway from the LHb GABAergic neurons to the posterior paraventricular thalamus. Activation of this pathway primarily mitigated pain-related behaviors, with minimal effects on anxiety. Conversely, interactions between GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons within the LHb were essential in alleviating both pain and anxiety following trigeminal nerve damage. Additionally, we identified that β-sitosterol interacts directly with LHb GABAergic neurons via the estrogen receptor α, providing dual therapeutic effects for both pain and anxiety. These findings highlight the critical role of reduced GABAergic neuronal activity in the LHb in the intersection of pain and anxiety, pointing to promising therapeutic possibilities.
Keywords: anxiety; neural circuit; pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

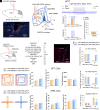
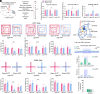

References
-
- Jarrin S., et al. , Optogenetics and its application in pain and anxiety research. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 105, 200–211 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Borsook D., et al. , Reward deficiency and anti-reward in pain chronification. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 68, 282–297 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Lucchetti G., et al. , Anxiety and fear-avoidance in musculoskeletal pain. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 16, 399–406 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82471243 81971056/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 82474629 82271258/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 82271248/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 82204830/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 2018SHZDZX01/Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

