METTL3 and IGF2BP2 coordinately regulate FOSL1 mRNA via m6A modification, suppressing trophoblast invasion and contributing to fetal growth restriction
- PMID: 39565355
- PMCID: PMC11578174
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202401665R
METTL3 and IGF2BP2 coordinately regulate FOSL1 mRNA via m6A modification, suppressing trophoblast invasion and contributing to fetal growth restriction
Abstract
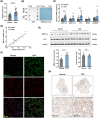
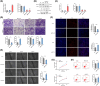
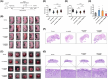
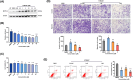
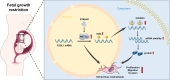
Fetal growth restriction (FGR) increases the risk of short-term and long-term complications. Widespread N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications on mRNAs have been found to be involved in various biological processes. However, the role of m6A modification in the pathogenesis of FGR remains elusive. Here, we report that elevated levels of METTL3 and m6A modification were detected in FGR placentae. Functionally, cell migration, invasion, and proliferation abilities were suppressed after METTL3 overexpression in HTR8/SVneo cells. Subsequently, methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeRIP-seq) and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) of METTL3-knockdown HTR8/SVneo cells were utilized together to identify FOSL1 as the downstream target genes of METTL3. Furthermore, we illustrated that METTL3-mediated m6A modification enhanced the expression of FOSL1 in a IGF2BP2 dependent manner. FOSL1 inhibited trophoblast invasion and migration. Importantly, STM2457, a novel METTL3 catalytic inhibitor, was intravenously administered to FGR mice models, which restore fetal and placental weights in vivo. In vitro STM2457 regulated trophoblast proliferation, invasion, and migration in a dose-dependent manner. In summary, this study reveals that METTL3 and IGF2BP2 increase FOSL1 expression in an m6A-dependent manner. The increase of FOSL1disrupts normal trophoblast invasion, which results in the progression of FGR. METTL3 can serve as a potential target for FGR therapy.
Keywords: FOSL1; METTL3; N6‐methyladenosine; STM2457; fetal growth restriction; trophoblast dysfunction.
© 2024 The Author(s). The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of METTL3 promotes mesangial cell mitophagy and attenuates glomerular damage by alleviating FOSL1 m6A modifications via IGF2BP2-dependent mechanisms.Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;236:116867. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.116867. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40081768
-
METTL3-dependent m6A modification of ERO1A mRNA regulates trophoblast migration and invasion in early-onset severe preeclampsia.Placenta. 2025 Aug;168:256-267. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2025.06.023. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Placenta. 2025. PMID: 40652673
-
circFTO binding with IGF2BP2 regulates trophoblast cells proliferation, migration, and invasion while mediating m6A modification of CCAR1 mRNA in spontaneous abortion.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2025 Jul 2;26(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12860-025-00546-8. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40604397 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3 as a master regulator of translation in cancer: mechanisms and implications.NAR Cancer. 2024 Mar 5;6(1):zcae009. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcae009. eCollection 2024 Mar. NAR Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38444581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGF2BP2: an m6A reader that affects cellular function and disease progression.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Apr 9;30(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00723-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40205577 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

