Unraveling the role of gut microbiota and immune cells in thyroid cancer and tumor drug resistance
- PMID: 39565441
- PMCID: PMC11579266
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01585-x
Unraveling the role of gut microbiota and immune cells in thyroid cancer and tumor drug resistance
Abstract
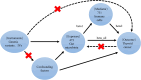
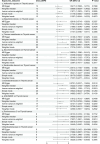
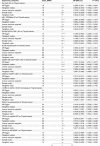
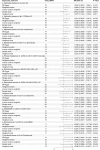
The gut microbiota (GM) and immune cells (IC) are increasingly recognized as key players in cancer development and progression. This study aimed to explore the potential mediating role of IC in the causal relationship between GM and thyroid cancer (TC) using Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis. Data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) encompassing 473 GM species, 731 IC types, and TC were utilized. MR analysis identified nine GM species with significant causal relationships to TC, mediated by 10 IC phenotypes such as "Switched Memory AC," "IgD-CD38dim AC," and "EM DN (CD4-CD8-) AC." These findings suggest a complex interplay where specific IC mediate the effects of GM on TC risk. Sensitivity analyses confirmed the robustness of these results, with no evidence of horizontal pleiotropy. This study highlights potential mechanisms linking GM and IC to TC, offering insights that could inform GM-based immunotherapeutic strategies and IC-targeted interventions. However, further experimental research is needed to validate these causal pathways and better understand the underlying biological mechanisms.
Keywords: Gut microbiota; Immune cells; Mediation analysis; Mendelian randomization; Thyroid cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune cells mediated the causal relationship between the gut microbiota and lung cancer: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Microbiol. 2024 May 3;15:1390722. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1390722. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38765682 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically predicted immune cells mediate the association between gut microbiota and neuropathy pain.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Oct;32(5):3357-3373. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01514-y. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38955934 Free PMC article.
-
Causal effects of gut microbiota, metabolites, immune cells, liposomes, and inflammatory proteins on anorexia nervosa: A mediation joint multi-omics Mendelian randomization analysis.J Affect Disord. 2025 Jan 1;368:343-358. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.09.115. Epub 2024 Sep 17. J Affect Disord. 2025. PMID: 39299582
-
Exploring the potential causal relationship between gut microbiota and heart failure: A two-sample mendelian randomization study combined with the geo database.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Feb;49(2):102235. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102235. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38040216 Review.
-
Gut microbiome versus thyroid cancer: Association and clinical implications (Review).Oncol Lett. 2025 May 27;30(1):368. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.15114. eCollection 2025 Jul. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40487754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang H, et al. Epigenetic signature associated with thyroid cancer progression and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;83:261–8. - PubMed
-
- Shobab L, Burman KD, Wartofsky L. Sex differences in differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2022;32(3):224–35. - PubMed
-
- Lin X, et al. Regulation of oncoprotein 18/Stathmin signaling by ERK concerns the resistance to taxol in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2016;31(2):37–43. - PubMed
-
- Ma PJ, Wang MM, Wang Y. Gut microbiota: a new insight into lung diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;155: 113810. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
