Investigation of differences between chronological and vascular age in persons with multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 39565794
- PMCID: PMC11578456
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311117
Investigation of differences between chronological and vascular age in persons with multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Objective: To determine vascular age (VA) in a cohort of persons with multiple sclerosis (PwMS) in Belgrade, Serbia, and to assess the difference between chronological age (CA) and VA, in this population.
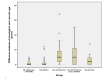
Material and methods: A case-control study was conducted at the Clinic of Neurology, University Clinical Center of Serbia in Belgrade. Study participants (n = 274) were recruited during regular outpatient visits. Demographic and clinical characteristics including the presence of CVD comorbidities of PwMS were collected. Data were obtained using a questionnaire, designed and adapted for the study purposes. Additionally, fasting blood samples were collected from all participants, in order to determine their lipid profile. VA was calculated based on the patient's sex, age, smoking status, total serum cholesterol level and systolic blood pressure (SBP) value. Afterwards, the study sample was divided into five groups with the different levels of the atherosclerotic burden, as follows: 1) PwMS without any CVD comorbidity; 2) PwMS with hyperlipidemia (HLP); 3) PwMS with HLP and hypertension (HTA); 4) PwMS with HLP, HTA and type 2 diabetes, and 5) PwMS with coronary artery disease (CAD). In the statistical analysis, for the determination of factors that are independently associated with the discrepancy between CA and VA in persons with MS, hierarchical regression analysis was performed.
Results: The mean values of CA and VA were statistically significantly different among the groups(p<0.001). Additionally, a significant difference was also detected between CA and VA (p<0.001). The highest VA (66.4±15.8 years) and the difference between CA and VA (6.5±7.3 years) were registered only in the group comprising PwMS, HPL, HTA and type 2 diabetes. Results of the hierarchical linear regression analysis showed that the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score, Body mass index (BMI), physical activity and the presence of type 2 diabetes, explained a total of 24% of the variations in the difference between CA and VA, in our cohort of MS patients.
Conclusion: Our study showed significant difference between CA and VA in PwMS and additionally, increasing VA with atherosclerotic burden. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that crucial factors which led to the occurrence of these differences were BMI, physical activity, EDSS and the presence of type 2 diabetes.
Copyright: © 2024 Maric et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- MS International Federation. 3rd edition of the Atlas of MS. Available online at: https://www.atlasofms.org/map/global/epidemiology/number-of-people-with-... (Accessed September 11, 2023).
-
- Corboy JR, Fox RJ, Kister I, Cutter GR, Morgan CJ, Seale R, et al.. Risk of new disease activity in patients with multiple sclerosis who continue or discontinue disease-modifying therapies (DISCOMS): a multicentre, randomised, single-blind, phase 4, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(7):568–577. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00154-0 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous