Nemvaleukin alfa, a modified interleukin-2 cytokine, as monotherapy and with pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors (ARTISTRY-1)
- PMID: 39567211
- PMCID: PMC11580269
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010143
Nemvaleukin alfa, a modified interleukin-2 cytokine, as monotherapy and with pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors (ARTISTRY-1)
Abstract
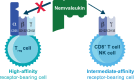
Background: Nemvaleukin alfa (nemvaleukin, ALKS 4230) is a novel, engineered cytokine that selectively binds to the intermediate-affinity interleukin-2 receptor, preferentially activating CD8+ T cells and natural killer cells, with minimal expansion of regulatory T cells, thereby mitigating the risk of toxicities associated with high-affinity interleukin-2 receptor activation. Clinical outcomes with nemvaleukin are unknown. ARTISTRY-1 investigated the safety, recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D), and antitumor activity of nemvaleukin in patients with advanced solid tumors.
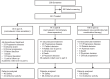
Methods: This was a three-part, open-label, phase 1/2 study: part A, dose-escalation monotherapy, part B, dose-expansion monotherapy, and part C, combination therapy with pembrolizumab. The study was conducted at 32 sites in 7 countries. Adult patients with advanced solid tumors were enrolled and received intravenous nemvaleukin once daily on days 1-5 (21-day cycle) at 0.1-10 µg/kg/day (part A), or at the RP2D (part B), or with pembrolizumab (part C). Primary endpoints were RP2D selection and dose-limiting toxicities (part A), and overall response rate (ORR) and safety (parts B and C).
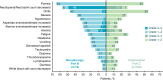
Results: From July 2016 to March 2023, 243 patients were enrolled and treated (46, 74, and 166 in parts A, B, and C, respectively). The maximum tolerated dose was not reached. RP2D was determined as 6 µg/kg/day. ORR with nemvaleukin monotherapy was 10% (7/68; 95% CI 4 to 20), with seven partial responses (melanoma, n=4; renal cell carcinoma, n=3). Robust CD8+ T and natural killer cell expansion, and minimal regulatory T cell expansion were observed following nemvaleukin treatment. ORR with nemvaleukin plus pembrolizumab was 13% (19/144; 95% CI 8 to 20), with 5 complete and 14 partial responses; 6 responses were in PD-(L)1 inhibitor-approved and five in PD-(L)1 inhibitor-unapproved tumor types. Three responses were in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. The most common grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) in parts B and C, respectively, were neutropenia (49%, 21%) and anemia (10%, 11%); 4% of patients in each part discontinued due to TRAEs.
Conclusions: Nemvaleukin was well tolerated and demonstrated promising antitumor activity across heavily pretreated advanced solid tumors. Phase 2/3 studies of nemvaleukin are ongoing.
Trial registration number: NCT02799095.
Keywords: Cytokine; Immunotherapy; Ovarian Cancer; Skin Cancer; Solid tumor.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: UNV declares research support from Bristol Myers Squibb and Merck; consulting fees from Alkermes, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Bayer, Gilead, Seattle Genetics, Pfizer, and Aveo; speaker honoraria fees from Exelixis, Bayer, and Pfizer. JM declares advisory board attendance and honoraria from Exelixis. IW declares participation in advisory board for GOG Partners; Travel/Honoraria fees from Regeneron and IIT Collaborative funding from Chimerix for trial purposes only. SDR declares stock ownership at Pfizer, Amgen, and Johnson & Johnson. CJH declares grants from Merck; consulting fees from Merck, Eisai, and Seagen; honoraria fees from Eisai, Seagen, and Astellas; and advisory board attendance for CRISPR and Seagen. AChauhan declares grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Clovis, Tersera, and ECS Progastrin; consulting fees from Tersera, Novartis, Lexicon, Ipsen, Curium, and Seneca Therapeutics; and honoraria from Tersera, Novartis, Lexicon, and Ipsen. AS declares funding to the institution from Alkermes. KDL declares funding to the institution from Alkermes and Merck; and employment with Regeneron. DSB declares independent research grant (payments made to institution) from AstraZeneca; consulting fees from or advisory board attendance for Bristol Myers Squibb, Mirati Therapeutics, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Amgen, Merck, Novocure, Regeneron, Syneos Health, Tempus and Daiichi-Sankyo; honoraria fees from AstraZeneca; advisory board attendance or travel fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novocure, AstraZeneca, Mirati Therapeutics and Regeneron; leadership as panel member for non-small cell lung cancer, thymic malignancies and pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma for National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). OD and MSE declare no conflicts of interest. DFM declares consulting fees from or advisory board attendance for Roche/Genentech BioOncology, Guidepoint, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Exelixis, Pfizer, Lovance, Werewolf Therapeutics, and Svnthekine; leadership at Beth Israel, Dana-Farber Harvard Cancer Center; committee service at Beth Israel, Dana-Farber Harvard Cancer Center; grant review for FDA, Dana-Farber Harvard Cancer Center, National Cancer Institute; and funding from Prometheus Laboratories, X4 Pharmaceuticals, Alkermes, NIH, and Dept of Defense. JFS declares consulting fees from Synlogic (institution) and Binhui Biopharmaceuticals (institution); leadership at Dialectic Therapeutics; stock ownership at AbbVie, Abbot, Bristol Myers Squibb, Intuitive Surgical, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and Regeneron. QSC declares grants from AstraZeneca; consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, AnHeart, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daichii Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Ocellaris, Pfizer, Roche, and Takeda; honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, AnHeart, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daichii Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Ocellaris, Pfizer, Roche, and Takeda; serving on data and safety monitoring board for Merck KgaA; and unpaid and medical advocacy leadership for Lung Cancer Canada. LG declares consulting fees from or advisory board attendance for Merck and GlaxoSmithKline; honoraria fees from Merck, AstraZeneca, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, Eisai-Merck, Novocure, and GOG; institutional research funding from Merck Sharp & Dohme, IMV, AstraZeneca, ImmunoGen, Tesaro/GlaxoSmithKline, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Alkermes, OncoQuest, Novocure, Esperas Pharma, Mersana, Roche, and K-Group Beta Inc. AChaudhry declares receiving grants or clinical trial contracts from Arcus, Boehringer Ingelheim, AbbVie, Exelixis, Medilink, Gilead, Seagen, BeiGene, Roche, Tvardi, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Henlius, Merck, Mersana, Eli Lilly, Zia Pharmaceuticals, and AstraZeneca. EC declares employment at START, HM Hospitales Group; leadership at START, PharmaMar, EORTC, Sanofi, BeiGene, Novartis, and Merus NV; stock and other ownership interests at START and Oncoart Associated; honoraria fees from HM Hospitales Group; consulting or advisory role at Nanobiotix, Janssen-Cilag, Roche/Genentech, TargImmune Therapeutics, Servier, Bristol Myers Squibb, Amunix, Adcendo, Anaveon, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Chugai Pharma, MonTa, MSD Oncology, Nouscom, Novartis, OncoDNA, T-Knife, Elevation Oncology, PharmaMar, Ellipses Pharma, Syneos Health, Genmab, and Diaccurate; research funding to the company from START; other relationships as president and founder of Foundation INTHEOS (Investigational Therapeutics in Oncological Sciences), not-for-profit foundation PharmaMar, and not-for-profit CRIS Cancer Foundation. RD declares previous employment at and stock ownership in Mural Oncology. VB declares institutional research funding from Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Loxo, Novartis, CytomX Therapeutics, Puma Biotechnology, Kura, Tesaro, Roche/Genentech, Bristol Myers Squibb, Menarini, Synthon, Janssen Oncology, Merck, Lilly, Merus, Pfizer, Bayer, Incyte, AbbVie, Zenith Epigenetics, Genmab, AstraZeneca, Adaptimmune, Alkermes, Amgen, Array BioPharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, BioNTech AG, and Boston Biomedical; consulting fees from OncoArt, and Guidepoint Global; honoraria fees from Loxo, Ideaya Biosciences, Puma Biotechnology, Amunix, Guidepoint Global, and EMD Serono; speakers’ bureau fees from Solti, Lilly, and Tactics; advisory board attendance or travel fees from START and Bayer; leadership at Next Oncology (Institution); stock ownership at 1TRIALSP; and employment at Quironsalud, Next Oncology. VV declares serving as a consultant or in an advisory role for Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, AstraZeneca, Regeneron, G1 Therapeutics, Amgen, GSK, and Novocure.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
