Totally Endoscopic Coronary Artery Bypass Graft: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Reconstructed Patient-Level Data
- PMID: 39567250
- PMCID: PMC11656624
- DOI: 10.1177/15569845241296530
Totally Endoscopic Coronary Artery Bypass Graft: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Reconstructed Patient-Level Data
Abstract
Objective: The standard approach for coronary artery bypass grafting is open surgery. Totally endoscopic coronary artery bypass has emerged as an alternative for selected patients. This meta-analysis sought to evaluate clinical outcomes with this emerging technique.
Methods: A PRISMA-compliant search was performed up to December 14, 2022, in PubMed (MEDLINE), Scopus, and Cochrane. Time-to-event data were reconstructed using Kaplan-Meier curves from source literature.
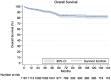
Results: A total of 2,774 patients with symptomatic coronary artery disease underwent totally endoscopic coronary artery bypass in 18 eligible studies. The mean patient age was 63.2 ± 12.3 years, and 77.5% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 72.2% to 82.4%) of the included patients were males. The mean operative time was 304.2 ± 155 min, whereas the mean internal mammary artery takedown time was 38.3 ± 18.4 min. Of the patients, 4.7% (95% CI: 1.6% to 9.1%) required conversions to open surgery. The 30-day complication rate was 5.9% (95% CI: 1.2% to 13.1%), whereas late complications developed in 4.8% (95% CI: 1.9% to 8.5%) of the patients. Freedom from major adverse cardiac events was 93.4% (95% CI: 85.3% to 94.8%) and 1-year, 5-year, and 10-year survival rates were 95.2%, 83.2%, and 81.7%, respectively. Reintervention was required in 3.3% (95% CI: 2.3% to 4.4%) of the cohort within a mean follow-up of 42.5 ± 27.8 months.
Conclusions: Totally endoscopic coronary artery bypass may be a safe and viable alternative for selected patients with coronary artery disease. Long-term follow-up will help define the place of robotic endoscopic treatment in the armamentarium of myocardial revascularization.
Keywords: CABG; cardiac surgery; coronary artery bypass graft; endoscopic; minimally invasive; robotic.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Preoperative coronary interventions for preventing acute myocardial infarction in the perioperative period of major open vascular or endovascular surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jul 3;7(7):CD014920. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014920.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38958136 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic Totally Endoscopic Reverse Hybrid Coronary Revascularization: Early and Midterm Outcomes.Innovations (Phila). 2025 May-Jun;20(3):276-282. doi: 10.1177/15569845251334117. Epub 2025 May 13. Innovations (Phila). 2025. PMID: 40359074
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation for coronary heart disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 6;11(11):CD001800. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001800.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34741536 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Meta-Analysis of First-Line Treatments for Unresectable Pleural Mesothelioma: Indirect Comparisons from Reconstructed Individual Patient Data of Six Randomized Controlled Trials.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 3;17(3):503. doi: 10.3390/cancers17030503. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941870 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Loulmet D, Carpentier A, d’Attellis N, et al.. Endoscopic coronary artery bypass grafting with the aid of robotic assisted instruments. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1999; 118: 4–10. - PubMed
-
- Leonard JR, Rahouma M, Abouarab AA, et al.. Totally endoscopic coronary artery bypass surgery: a meta-analysis of the current evidence. Int J Cardiol 2018; 261: 42–46. - PubMed
-
- Göbölös L, Ramahi J, Obeso A, et al.. Robotic totally endoscopic coronary artery bypass grafting: systematic review of clinical outcomes from the past two decades. Innovations 2019; 14: 5–16. - PubMed
-
- Mishra YK, Wasir H, Sharma KK, et al.. Totally endoscopic coronary artery bypass surgery. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 2006; 14: 447–451. - PubMed
-
- Balkhy HH, Wann LS, Krienbring D, et al.. Integrating coronary anastomotic connectors and robotics toward a totally endoscopic beating heart approach: review of 120 cases. Ann Thorac Surg 2011; 92: 821–827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

